Page 313 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 313
Observe that if A is the standard matrix for T, then 7 can be written as
from which it follows that
The eigenvalues of T are precisely the eigenvalues of its standard matrix A.
x is an eigenvector of T corresponding to if and only if x is an eigenvector of A corresponding to .
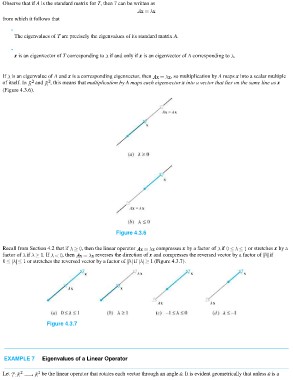
If is an eigenvalue of A and x is a corresponding eigenvector, then , so multiplication by A maps x into a scalar multiple
of itself. In and , this means that multiplication by A maps each eigenvector x into a vector that lies on the same line as x
(Figure 4.3.6).
Figure 4.3.6
Recall from Section 4.2 that if , then the linear operator compresses x by a factor of if or stretches x by a
factor of if . If , then reverses the direction of x and compresses the reversed vector by a factor of if
or stretches the reversed vector by a factor of if (Figure 4.3.7).
Figure 4.3.7
EXAMPLE 7 Eigenvalues of a Linear Operator
Let be the linear operator that rotates each vector through an angle . It is evident geometrically that unless is a