Page 625 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 625
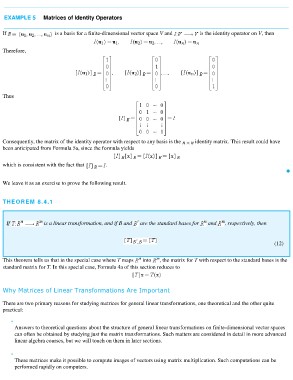
EXAMPLE 5 Matrices of Identity Operators is the identity operator on V, then
If is a basis for a finite-dimensional vector space V and
Therefore,
Thus
Consequently, the matrix of the identity operator with respect to any basis is the identity matrix. This result could have
been anticipated from Formula 5a, since the formula yields
which is consistent with the fact that .
We leave it as an exercise to prove the following result.
THEOREM 8.4.1
If is a linear transformation, and if B and are the standard bases for and , respectively, then
(12)
This theorem tells us that in the special case where T maps into , the matrix for T with respect to the standard bases is the
standard matrix for T. In this special case, Formula 4a of this section reduces to
Why Matrices of Linear Transformations Are Important
There are two primary reasons for studying matrices for general linear transformations, one theoretical and the other quite
practical:
Answers to theoretical questions about the structure of general linear transformations on finite-dimensional vector spaces
can often be obtained by studying just the matrix transformations. Such matters are considered in detail in more advanced
linear algebra courses, but we will touch on them in later sections.
These matrices make it possible to compute images of vectors using matrix multiplication. Such computations can be
performed rapidly on computers.