Page 621 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 621
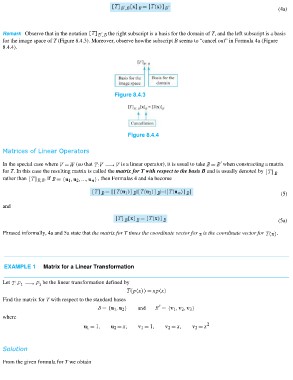
(4a)
Remark Observe that in the notation the right subscript is a basis for the domain of T, and the left subscript is a basis
for the image space of T (Figure 8.4.3). Moreover, observe howthe subscript B seems to “cancel out” in Formula 4a (Figure
8.4.4).
Figure 8.4.3
Figure 8.4.4
Matrices of Linear Operators
In the special case where (so that is a linear operator), it is usual to take when constructing a matrix
for T. In this case the resulting matrix is called the matrix for T with respect to the basis B and is usually denoted by
rather than . If , then Formulas 4 and 4a become
(5)
and
Phrased informally, 4a and 5a state that the matrix for T times the coordinate vector for is the coordinate vector for (5a)
.
EXAMPLE 1 Matrix for a Linear Transformation
Let be the linear transformation defined by
Find the matrix for T with respect to the standard bases
where
Solution
From the given formula for T we obtain