Page 10 - Lecture Notes DCC3113
P. 10
The method of construction for Macadam roads
i. Sub-grade was prepared and compacted to the required width of the road.
ii. Prepared sub-grade with a camber
iii. Construction of road consists of three layers: foundation layer, intermediate layer and wearing
surface layer.
iv. Cross slope of finished surface was kept as 1 in 36.
v. Macadam method was first scientific method based on modern concepts and hence is still in use
in most parts of the world.
The historical road development can be divided in to the following era:
i. Early/ Basic roads
ii. Roman roads
iii. Modern roads
Early/ Basic roads
The needs of road started from the invention of wheel in Samaria in 3000 BC. Among the early
road inventions in many parts of the world were:
China Dynasty – ‘China Silk Route’ was the first road built around 2600 BC. The road was used
to transport silk and elephant tusks between China and India
Persian Empire – Big trade involving import and export such as silk, porcelain and wood crafts
between China and Europe.
Britain – ‘Raft Road’ believed was built around 2500 BC
India – Indus Valley where roads made of bricks with drainage system equipped with pipe
Mesopotamia and Egypt – Brick road and asphalt road was found in Babylon and mountainous
area of Mesopotamia. In Egypt, the road was built to transport block of rock to construct pyramid
Roman Road
Roman’s developed very elaborate system of
roads mainly for the purpose of military movement.
They constructed in all about one lakh kilometres of road,
extending in whole of their empire. An important road
constructed by Romans in 312 B.C called Appian way is
still in existence in Rome.
Figure 1-7: Roman Road
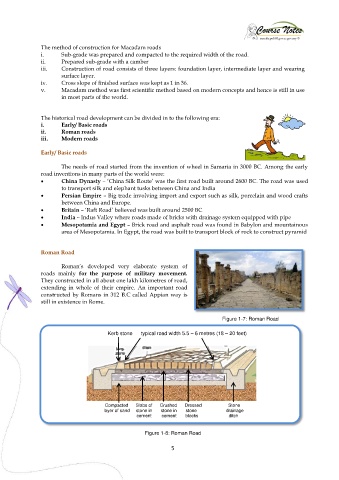
Kerb stone typical road width 5.5 – 6 metres (18 – 20 feet)
Compacted Slabs of Crushed Dressed Stone
layer of sand stone in stone in stone drainage
cement cement blocks ditch
Figure 1-8: Roman Road
5