Page 132 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 132
108 Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy
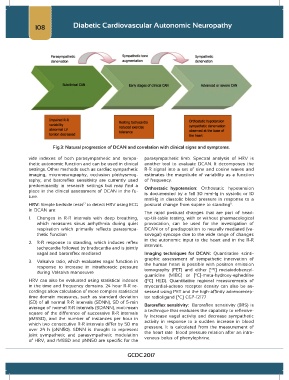
Fig.3: Natural progression of DCAN and correlation with clinical signs and symptoms.
vide indexes of both parasympathetic and sympa- parasympathetic limb. Spectral analysis of HRV is
thetic autonomic function and can be used in clinical another tool to evaluate DCAN. It decomposes the
settings. Other methods such as cardiac sympathetic R-R signal into a set of sine and cosine waves and
imaging, microneurography, occlusion plethysmog- estimates the magnitude of variability as a function
raphy, and baroreflex sensitivity are currently used of frequency.
predominantly in research settings but may find a Orthostatic hypotension: Orthostatic hypotension
place in the clinical assessment of DCAN in the fu- is documented by a fall 30 mmHg in systolic or 10
ture.
mmHg in diastolic blood pressure in response to a
HRV: Simple bedside tests to detect HRV using ECG postural change from supine to standing .
11
12
in DCAN are:
The rapid postural changes that are part of head-
1. Changes in R-R intervals with deep breathing, up-tilt-table testing, with or without pharmacological
which measures sinus arrhythmia during quiet provocation, can be used for the investigation of
respiration which primarily reflects parasympa- DCAN or of predisposition to neurally mediated (va-
thetic function sovagal) syncope due to the wide range of changes
in the autonomic input to the heart and in the R-R
2. R-R response to standing, which induces reflex
tachycardia followed by bradycardia and is jointly intervals.
vagal and baroreflex mediated Imaging techniques for DCAN: Quantitative scinti-
graphic assessment of sympathetic innervation of
3. Valsalva ratio, which evaluates vagal function in the human heart is possible with positron emission
response to increase in intrathoracic pressure tomography (PET) and either [ I] metaiodobenzyl-
123
during Valsalva manoeuvre
guanidine (MIBG) or [ C]-meta-hydroxy-ephedrine
11
HRV can also be evaluated using statistical indexes ([ C] HED). Quantitative regional measurements of
11
in the time and frequency domains. 24 hour R-R re- myocardial-adreno receptor density can also be as-
cordings allow calculation of more complex statistical sessed using PET and the high-affinity–adrenorecep-
time domain measures, such as standard deviation tor radioligand [ C] CGP-12177
11
(SD) of all normal R-R intervals (SDNN), SD of 5-min Baroreflex sensitivity: Baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) is
average of normal R-R intervals (SDANN), root-mean a technique that evaluates the capability to reflexive-
square of the difference of successive R-R intervals ly increase vagal activity and decrease sympathetic
(rMSSD), and the number of instances per hour in activity in response to a sudden increase in blood
which two consecutive R-R intervals differ by 50 ms pressure. It is calculated from the measurement of
over 24 h (pNN50). SDNN is thought to represent the heart rate– blood pressure relation after an intra-
joint sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation venous bolus of phenylephrine.
of HRV, and rMSSD and pNN50 are specific for the
GCDC 2017