Page 35 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 35
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 11
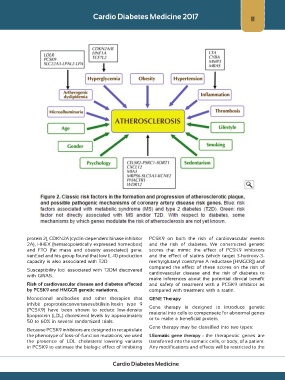
protein 2), CDKN2A (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor PCSK9 on both the risk of cardiovascular events
2A), HHEX (hematopoietically expressed homeobox) and the risk of diabetes. We constructed genetic
and FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) gene. scores that mimic the effect of PCSK9 inhibitors
vanExel and his group found that low IL-10 production and the effect of statins (which target 3-hydroxy-3-
capacity is also associated with T2D methylglutaryl–coenzyme A reductase [HMGCR]) and
compared the effect of these scores on the risk of
Susceptibility loci associated with T2DM discovered cardiovascular disease and the risk of diabetes to
with GWAS.
make inferences about the potential clinical benefit
Risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes affected and safety of treatment with a PCSK9 inhibitor as
by PCSK9 and HMGCR genetic variations. compared with treatment with a statin.
Monoclonal antibodies and other therapies that GENE Therapy
inhibit proproteinconvertasesubtilisin–kexin type 9
(PCSK9) have been shown to reduce low-density Gene therapy is designed to introduce genetic
lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels by approximately material into cells to compensate for abnormal genes
50 to 60% in several randomized trials. or to make a beneficial protein.
Gene therapy may be classified into two types:
Because PCSK9 inhibitors are designed to recapitulate
the phenotype of loss-of-function mutations, we used 1.Somatic gene therapy - the therapeutic genes are
the presence of LDL cholesterol–lowering variants transferred into the somatic cells, or body, of a patient.
in PCSK9 to estimate the biologic effect of inhibiting Any modifications and effects will be restricted to the
Cardio Diabetes Medicine