Page 373 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 373
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 349
References.
1. Hagan AD, Alpert JS. Evaluation of computer programs for clinical elec-
trocardiography. In: Cady L, ed. Computer Techniques in Cardiology.New
York: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 1976:77-96.
2. MMilliken JA et al, Impact of an ECG computer analysis program on the
cardiologist’s interpretation, J Electrocardiol, 1983 April (62); 141-149
3. Pordy, L. Computer analysis of cardiac arrhythmias. Cardiovasc
lin. 1970;2:281–293.
4. Milliken, J.A., Wartak, J., Lywood, D.W. et al, Validity of computer
interpretation of electrocardiogram.Can Med Assoc J. 1971;104:1147–
1150.
5. Bailey, J.J., Itscoitz, S.B., Grauer, L.E. et al, A method for evaluating
computer programs for electrocardiographic interpretation. II. Mayo
Clinic program of 1968. Circulation. 1974;50:80–87
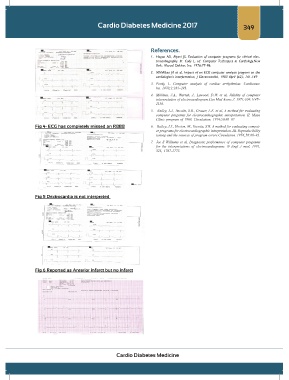
Fig 4- ECG has completely missed an RBBB 6. Bailey, J.J., Horton, M., Itscoitz, S.B. A method for evaluating comput-
er programs for electrocardiographic interpretation. III. Reproducibility
testing and the sources of program errors.Circulation. 1974;50:88–93.
7. Joe S Williams et al, Diagnostic performance of computer programs
for the interpretations of electrocardiograms. N Engl J med, 1991,
325, 1767-1773.
Fig 5 Dextrocardia is not interpreted
Fig 6 Reported as Anterior infarct but no infarct
Cardio Diabetes Medicine