Page 435 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 435
DM Management in Special Situations 411
Post Renal Transplant and Post CABG
tient’s metabolism is in steady statewith reasonable arately and thus offers greater flexibility. Hence it is
pre-operative blood glucose levels; hence it should better used in severely uncontrolled, brittle patients
not be used in severely hyperglycemic, unstable or or in special circumstances like CABG surgery. This
brittle patients. After the start of the infusion the system needs more dosage adjustments than the
blood glucose levels are monitored hourly. Special GKI regimen Overall outcome with regards to glycae-
caution needs to be taken in patients with compro- mic control, hypoglycaemic events, post- operative
mised renal function or those on ACE inhibitors.The infection rates and duration of stay in hospital was
GKI regimen is considerably simpler and because similar to GKI regimen.
insulin is given in balanced proportion the infusion After surgery patient often develops hypoglycaemia,
rate is not so critical.
which might go undetected. As soon as the patient
II. Separate line approach: In this system, one infusion is able to eat, we can restart subcutaneous injections
line is used to deliver 10% dextrose solution at 100ml/ of insulin. The i.v. insulin should be discontinued after
hr preferably using a high precision pump while the about one hour of resumption of subcutaneous insu-
soluble insulin infusion can be given either through lin injection. The insulin requirement increases over
a separate vein or ‘piggy-backed’ (preferable) into the baseline requirements on the day of surgery and the
glucose line and the rate is titrated to maintain blood first two postoperative days and usually comes down
glucose in target range. This facilitates the ability to to normal levels on the third post-operative day in
5
make changes in the insulin or glucose infusion sep- an otherwise uncomplicated surgery. The mean in-
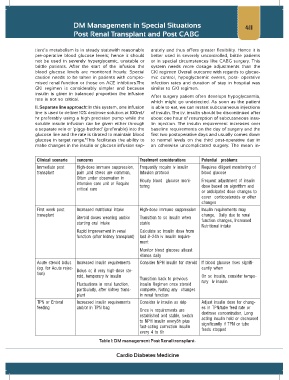
Clinical scenario concerns Treatment considerations Potential problems
Immediate post High-dose immune suppression, Frequently require iv insulin Requires diligent monitoring of
transplant pain ,and stress are common, Infusion protocol blood glucose
Often under observation in Hourly blood glucose moni- Frequent adjustment of insulin
intensive care unit or Require toring dose based on algorithm and
critical care
or anticipated dose changes to
cover corticosteroids or other
changes
First week post Increased nutritional intake High-dose immuno suppression Insulin requirements may
transplant change, Daily due to renal
Steroid doses weaning and/or Transition to sc insulin when function changes, Increased
starting oral intake stable
Nutritional intake
Rapid improvement in renal Calculate sc insulin dose from
function (after kidney transplant) last 8–24h iv insulin require-
ment
Monitor blood glucose atleast
4times daily
Acute steroid bolus Increased insulin requirements Consider NPH insulin for steroid If blood glucose rises signifi-
(eg. for Acute rejec- Bolus or, if very high-dose ste- cantly when
tion)
roid, temporary iv insulin On sc insulin, consider tempo-
Transition back to previous
Fluctuations in renal function, insulin Regimen once steroid rary iv insulin
particularly, after kidney trans- complete, Noting any changes
plant in renal function
TPN or Enteral Increased insulin requirements Consider iv insulin as drip Adjust insulin dose for chang-
feeding and/or in TPN bag es in TPN/tube feed rate or
Once iv requirements are
established and stable, switch dextrose concentration, Long
to NPH insulin every8h plus acting insulin held or decreased
fast-acting correction insulin significantly if TPN or tube
every 4 to 6h feeds stopped
Table 1: DM management Post Renal transplant-
Cardio Diabetes Medicine