Page 549 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 549
Integrated Management of 525
Diabetes Through Novel Therapies
of the Islets of Langerhans. MSCs are known to pro- F)-BB, and angiopoietin-1, also play an integral role
mote the regeneration of pancreatic islet beta cells, in the process of cell regeneration.
protect endogenous pancreatic islet beta cells from Type 1 Diabetes is characterized by the action of
apoptosis, and ameliorate insulin resistance of pe- b-cell-specific, autoreactive T-cells. Even if the regen-
ripheral tissues by providing a supportive niche mi- erative properties of the pancreas remain functional,
croenvironment driven by the secretion of paracrine the continued presence of these T-cells effectively
factors or the deposition of extracellular matrix.
counteracts any endogenous repair and would likely
The identification of stem cells that possess the po- decimate populations of newly-regenerated or trans-
tential to differentiate into insulin-producing cells planted insulin-producing cells (5).
(IPCs), improve pancreatic regeneration, and amelio- In addition to their regenerative properties, MSCs
rate insulin resistance offers an alternative to islet have also demonstrated an immunoregulatory ca-
cell transplant. The potential to differentiate into IPCs pacity. MSCs are also known as immunoprivileged
was first considered to be the primary mechanism cells because of the low intracellular expression of
by which MSCs ameliorate hyperglycemia in T2DM. class II major histocompatibility (MHC) proteins and
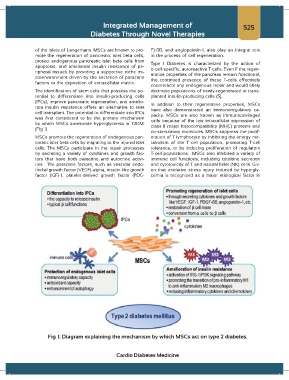
(Fig 1)
co-stimulatory molecules. MSCs suppress the prolif-
MSCs promote the regeneration of endogenous pan- eration of T lymphocyte by inhibiting the energy me-
creatic islet beta cells by migrating to the injured islet tabolism of the T cell population, promoting T-cell
cells. The MSCs participate in the repair processes tolerance, or by inducing proliferation of regulatory
by secreting a variety of cytokines and growth fac- T-cell populations. MSCs also inhibited a variety of
tors that have both paracrine and autocrine activi- immune cell functions, including cytokine secretion
ties. The paracrine factors, such as vascular endo- and cytotoxicity of T and natural killer (NK) cells. Giv-
thelial growth factor (VEGF)-alpha, insulin-like growth en that oxidative stress injury induced by hypergly-
factor (IGF)-1, platelet-derived growth factor (PDG- cemia is recognized as a major etiological factor in
Fig 1: Diagram explaining the mechanism by which MSCs act on type 2 diabetes.
Cardio Diabetes Medicine