Page 630 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 630
606 Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Make In India
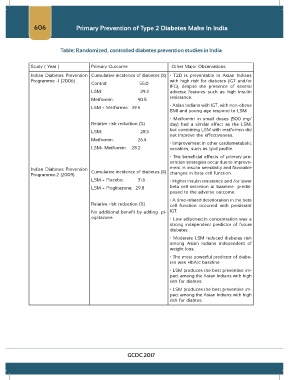
Table: Randomized, controlled diabetes prevention studies in India
Study ( Year ) Primary Outcome Other Major Observations
Indian Diabetes Prevention Cumulative incidence of diabetes (%) • T2D is preventable in Asian Indians
Programme -1 (2006) with high risk for diabetes (IGT and/or
Control: 55.0
IFG), despite the presence of several
LSM: 39.3 adverse features such as high insulin
resistance.
Metformin: 40.5
• Asian Indians with IGT, with non-obese
LSM + Metformin: 39.5
BMI and young age respond to LSM.
• Metformin in small doses (500 mg/
Relative risk reduction (%) day) had a similar effect as the LSM,
but combining LSM with metformin did
LSM: 28.5
not improve the effectiveness.
Metformin: 26.4
• Iimprovement in other cardiometabolic
LSM+ Metformin: 28.2 variables, such as lipid profile.
• The beneficial effects of primary pre-
vention strategies occur due to improve-
Indian Diabetes Prevention Cumulative incidence of diabetes (%) ment in insulin sensitivity and favorable
Programme-2 (2009) changes in beta cell function.
LSM + Placebo: 31.6 • Higher insulin resistance and /or lower
LSM + Pioglitazone: 29.8 beta cell secretion at baseline predis-
posed to the adverse outcome.
• A time-related deterioration in the beta
Relative risk reduction (%) cell function occurred with persistant
No additional benefit by adding pi- IGT.
oglitazone • Low adiponectin concentration was a
strong independent predictor of future
diabetes .
• Moderate LSM reduced diabetes risk
among Asian Indians independent of
weight loss.
• The most powerful predictor of diabe-
tes was HbA1c baseline.
• LSM produces the best preventive im-
pact among the Asian Indians with high
risk for diabtes.
• LSM produces the best preventive im-
pact among the Asian Indians with high
risk for diabtes.
GCDC 2017