Page 64 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 64
40 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
ROLE OF ABPM IN DIABETIC PATIENTS 5,6
- ABPM is advisable in all diabetic patients with
high-normal BP
- Diabetic patients are more likely to have
- White-coat hypertension
- Masked hypertension
- Nondipping
- Reverse dipping
- Morning BP surge
- High prevalence of masked hypertension in dia-
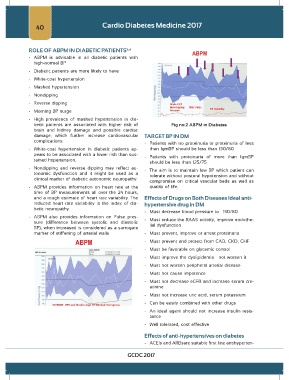
betic patients are associated with higher risk of Fig no:2 ABPM in Diabetes
brain and kidney damage and possible cardiac
damage, which further increase cardiovascular TARGET BP IN DM
complications.
- Patients with no proteinuria or proteinuria of less
- White-coat hypertension in diabetic patients ap- than 1gmBP should be less than 130/80
pears to be associated with a lower risk than sus- - Patients with proteinuria of more than 1gmBP
tained hypertension.
should be less than 125/75
- Nondipping and reverse dipping may reflect au- - The aim is to maintain low BP which patient can
tonomic dysfunction and it might be used as a tolerate without postural hypotension and without
clinical marker of diabetic autonomic neuropathy.
compromise on critical vascular beds as well as
- ABPM provides information on heart rate at the quality of life.
time of BP measurements all over the 24 hours,
and a rough estimate of heart rate variability. The Effects of Drugs on Both Diseases Ideal anti-
reduced heart rate variability is the index of dia- hypertensive drug in DM
betic neuropathy.
- Must decrease blood pressure to ≤ 130/80
- ABPM also provides information on Pulse pres- - Must reduce the RAAS activity, improve endothe-
sure (difference between systolic and diastolic lial dysfunction
BP), when increased is considered as a surrogate
marker of stiffening of arterial walls - Must prevent, improve or arrest proteinuria
- Must prevent and protect from CAD, CKD, CHF
- Must be favorable on glycemic control
- Must improve the dyslipidemia – not worsen it
- Must not worsen peripheral arterial disease
- Must not cause impotence
- Must not decrease eGFR and increase serum cre-
atinine
- Must not increase uric acid, serum potassium
- Can be easily combined with other drugs
- An ideal agent should not increase insulin resis-
tance
- Well tolerated, cost effective
Effects of anti-hypertensives on diabetes
- ACEIs and ARBsare suitable first line antihyperten-
GCDC 2017