Page 661 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 661
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 637
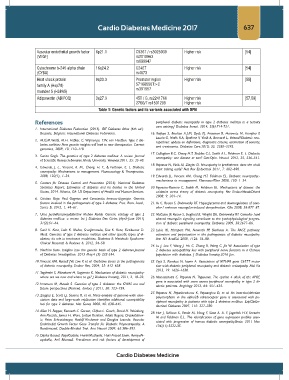
Vascular endothelial growth factor 6p21.1 C936T / rs3025039 Higher risk [54]
(VEGF) rs2010963
rs699947
Cytochrome b-245 alpha chain 16q24.2 C242T Higher risk [54]
(CYBA) rs4673
Heat shock protein 9q33.3 Promoter region Higher risk [55]
family A (Hsp70) 57168556T>C
member 5 (HSPA5) rs391957
Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) 3q27.3 45T / G, rs2241766 Higher risk [57,58]
276G/T rs1501299 Higher risk
Table 1: Genetic factors and its variants associated with DPN
References peripheral diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary
1. International Diabetes Federation (2013). IDF Diabetes Atlas (6th ed.). care setting.J Diabetes Invest. 2014, 5(6):714-721.
Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation. 16. Tesfaye S, Boulton A.J.M, Dyck P.J, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P,
Lauria G, Malik R.A, Spallone V, Vinik A, Bernardi L, ValensiP.Diabetic neu-
2. M.G.M.Wolfs, M.H. Hofker, C. Wijmenga, T.W. van Haeften. Type 2 dia- ropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity,
betes mellitus: New genetic insights will lead to new therapeutics. Current and treatments. Diabetes Care.2010; 33, 2285–2293.
genomics, 2009, 10: 110–118
17. Callaghan B.C, Cheng H.T, Stables C.L, Smith A.L, Feldman E. L. Diabetic
3. Sunita Singh. The genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. Journal neuropathy: one disease or two? Curr.Opin. Neurol. 2012, 25, 536–541.
of Scientific Research.Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi.2011, 55: 35-48.
18. Papanas N, Vinik AI, Ziegler D. Neuropathy in prediabetes: does the clock
4. Edwards, J. L., Vincent, A. M., Cheng, H. T., & Feldman, E. L. Diabetic start ticking early? Nat Rev Endocrinol 2011, 7: 682–690.
neuropathy: Mechanisms to management. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,
2008, 120(1), 1–34. 19. Edwards JL, Vincent AM, Cheng HT, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy:-
mechanisms to management. PharmacolTher 2008, 120: 1–34.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2014). National Diabetes
Statistics Report: Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United 20. Figueroa-Romero C, Sadidi M, Feldman EL. Mechanisms of disease: the
States, 2014. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services. oxidative stress theory of diabetic neuropathy. Rev EndocrMetabDisord
2008, 9: 301–14.
6. Cristian Guja, Paul Gagniuc and Constantin Ionescu-tîrgovişte. Genetic
factors involved in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Proc. Rom. Acad., 21. Yu C, Rouen S, Dobrowsky RT. Hyperglycemia and downregulation of cave-
Series B, 2012, 1, 44–61. olin-1 enhance neuregulin-induced demyelination. Glia 2008, 56:877–87.
7. Uma JyothiKommoju&Battini Mohan Reddy. Genetic etiology of type 2 22. McGuire JF, Rouen S, Siegfreid E, Wright DE, Dobrowsky RT. Caveolin-1and
diabetes mellitus: a review. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (April–June 2011) altered neuregulin signaling contribute to the pathophysiological progres-
31(2):51–64. sion of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes 2009, 58:2677–86.
8. Sunil K. Kota, Lalit K. Meher, SrutiJammula, Siva K. Kota, Kirtikumar D. 23. Lukic IK, Humpert PM, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A. The RAGE pathway:
Modi. Genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus and other specific types of di- activation and perpetuation in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy.
abetes; its role in treatment modalities. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Ann NY AcadSci 2008, 1126: 76–80.
Clinical Research & Reviews 6, 2012, 54–58.
24. Lu J, Luo Y, Wang J, Hu C, Zhang R, Wang C, Jia W. Association of type
9. Norihiro Kato. Insights into the genetic basis of type 2 diabetes.Journal 2 diabetes susceptibility loci with peripheral nerve function in a Chinese
of Diabetes Investigation. 2013 May.4 (3) 233-244. population with diabetes. J Diabetes Investig.2016 Jun.
10. Vincent AM, Russell JW, Low P, et al. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis 25. Yigit S, Karakus N, Inanir A. Association of MTHFR gene C677T muta-
of diabetic neuropathy. Endocr Rev, 2004, 25: 612–628. tion with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic retinopathy. Mol Vis
2013, 19: 1626–1630.
11. Yagihashi S, Mizukami H, Sugimoto K. Mechanism of diabetic neuropathy:
where are we now and where to go? J Diabetes Investig, 2011, 2, 18–32. 26. Monastiriotis C, Papanas N, Trypsianis. The epsilon 4 allele of the APOE
gene is associated with more severe peripheral neuropathy in type 2 di-
12. Imamura M, Maeda S. Genetics of type 2 diabetes: the GWAS era and abetic patients. Angiology 2013, 64: 451–455.
future perspectives [Review]. Endocr J 2011, 58: 723–739.
27. Papanas N, Papatheodorou K, Papazoglou D, et al. An insertion/deletion
13. Zeggini E, Scott LJ, Saxena R, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide asso- polymorphism in the alpha2B adrenoceptor gene is associated with pe-
ciation data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility ripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. ExpClinEn-
loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2008, 40: 638–645. docrinol Diabetes 2007, 115: 327–330.
14. Allan H. Ropper, Kenneth C. Gorson, Clifton L. Gooch, David H. Weinberg, 28. Hur J, Sullivan K, Pande M, Hong Y, Sima A. A. F, Jagadish H.V, Kretzler
Ann Pieczek, James H. Ware, Joshua Kershen, Adam Rogers, DraskoSimov- M and Feldman E.L. The identification of gene expression profiles asso-
ic, Peter Schratzberger, Rudolf Kirchmair and Douglas Losordo. Vascular ciated with progression of human diabetic neuropathy.Brain. 2011 Nov,
Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Transfer for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: A 134(11):3222-35.
Randomized, Double-Blinded Trial. Ann Neurol 2009, 65:386–393.
15. Dipika Bansal, KapilGudala, HariniMuthyala, Hari Prasad Esam, RamyaN-
ayakallu, Anil Bhansali. Prevalence and risk factors of development of
Cardio Diabetes Medicine