Page 80 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 80
56 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
tion according to the state of extremities and lungs
(9)
Syncope Irregular pulse
helps in understanding the severity of heart failure
Trepopnoea Tachypnoea
and need for immediate action. Framingham devised
Cheyne Stokes respiration criteria for recognising heart failure which includes
(10)
Hepatomegaly distended neck veins, cold extremities, gallop rhythm
Ascites or new onset murmur on cardiovascular system ex-
amination, bilateral rales in the lungs, altered mental
Cold extremities
status, hepatomegaly, pedal edema and/or oliguria.
Oliguria
Other positive findings are tachycardia, narrow pulse
Narrow pulse pressure pressure, S3 and S4 gallops and murmurs of mitral
(Table 1) Symptoms And Signs of Cardiogenic Shock and/or tricuspid regurgitation.
The suddenness of onset of shock may help in look- Critically ill patients have to be stabilized with respect
ing for new onset causes of cardiogenic shock like to securing airway, breathing and circulation. Early
myocardial infarction or myocarditis. History of cor- investigations should be directed to rule out obstruc-
onary artery disease or acute coronary syndrome or tive forms of cardiogenic shock like tension pneumo-
pre-existing cardiomyopathy is useful in delineating thorax, cardiac tamponade or pulmonary embolism.
the probable etiology of cardiogenic shock. Initial blood investigations include arterial blood gas-
es, hemoglobin, cardiac troponins, brain natriuretic
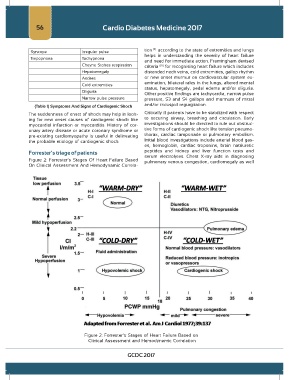
Forrester’s triage of patients peptides and kidney and liver function tests and
serum electrolytes. Chest X-ray aids in diagnosing
Figure 2: Forrester’s Stages Of Heart Failure Based pulmonary venous congestion, cardiomegaly as well
On Clinical Assessment And Hemodynamic Correla-
Figure 2: Forrester’s Stages of Heart Failure Based on
Clinical Assessment and Hemodynamic Correlation
GCDC 2017