Page 78 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 78
54 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
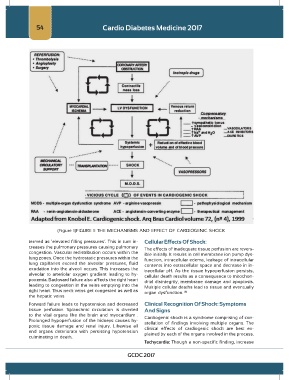
(Figure 1)FIGURE 1: THE MECHANISMS AND EFFECT OF CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
termed as ‘elevated filling pressures’. This in turn in- Cellular Effects Of Shock:
creases the pulmonary pressures causing pulmonary The effects of inadequate tissue perfusion are revers-
congestion. Vascular redistribution occurs within the ible initially. It results in cell membrane ion pump dys-
lung zones. Once the hydrostatic pressures within the function, intracellular edema, leakage of intracellular
lung capillaries exceed the alveolar pressures, fluid contents into extracellular space and decrease in in-
exudation into the alveoli occurs. This increases the tracellular pH. As the tissue hypoperfusion persists,
alveolar to arteriolar oxygen gradient leading to hy- cellular death results as a consequence to mitochon-
poxemia. Backward failure also affects the right heart drial disintegrity, membrane damage and apoptosis.
leading to congestion in the veins emptying into the Multiple cellular deaths lead to tissue and eventually
right heart. Thus neck veins get congested as well as organ dysfunction. (8)
the hepatic veins.
Forward failure leads to hypotension and decreased Clinical Recognition Of Shock: Symptoms
tissue perfusion. Splanchnic circulation is diverted And Signs
to the vital organs like the brain and myocardium . Cardiogenic shock is a syndrome comprising of con-
Prolonged hypoperfusion of the kidneys causes hy- stellation of findings involving multiple organs. The
poxic tissue damage and renal injury. Likewise all clinical effects of cardiogenic shock are best ex-
end organs deteriorate with persisting hypotension plained by each of the organs involved in the process.
culminating in death.
Tachycardia: Though a non-specific finding, increase
GCDC 2017