Page 252 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 252
Example 3
What is the maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted when a monochromatic light
(l = 550 nm) is shone on a metal which has a work function of 2.00 eV?
[Given hc = 1.243 × 10 eV nm, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10 J, mass of electron, m = 9.11 × 10 kg]
3
–19
–31
Solution
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
Wavelength, l = 550 nm
3
hc = 1.243 × 10 eV nm
–19
1 eV = 1.60 × 10 J
Mass of electron, m = 9.11 × 10 kg
–31
E = hc Then 1 mv 2 = 2.26 – 2.00
l 2 max = 0.26 eV
3
= 1.243 × 10 eV nm 1
550 nm mv 2 = 0.26 × 1.60 × 10 J
–19
= 2.26 eV 2 max = 4.16 × 10 J
–20
=
v max ! 2 × 4.16 × 10 –20
–31
9.11 × 10
= 3.02 × 10 m s –1
5
Example 4
When a photocell is shone on with a red light (l = 750 nm) and then with a blue light
1
(l = 460 nm), the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted by the blue
2
light is two times that of the red light.
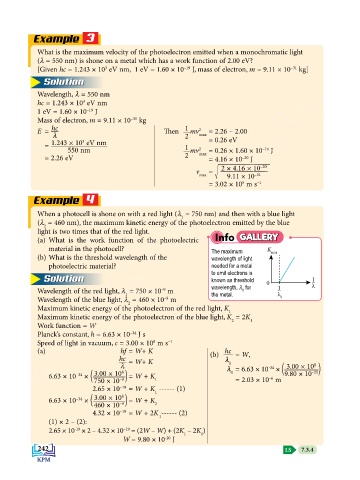
(a) What is the work function of the photoelectric Info GALLERY
material in the photocell? The maximum K max
(b) What is the threshold wavelength of the wavelength of light
photoelectric material? needed for a metal
to emit electrons is
Solution known as threshold 0 1
–
wavelength, l for 1 λ
Wavelength of the red light, l = 750 × 10 m the metal. 0 – λ
–9
1
Wavelength of the blue light, l = 460 × 10 m 0
–9
2
Maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron of the red light, K 1
Maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron of the blue light, K = 2K 1
2
Work function = W
–34
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 × 10 J s
Speed of light in vacuum, c = 3.00 × 10 m s –1
8
(a) hf = W+ K (b) hc = W,
hc = W+ K l
l l = 6.63 × 10 × ( 3.00 × 10 –20)
0
8
-34
8
–34
6.63 × 10 × ( 3.00 × 10 –9) = W + K 1 0 = 2.03 × 10 m 9.80 × 10
–6
750 × 10
2.65 × 10 = W + K ------ (1)
–19
1
8
6.63 × 10 × ( 3.00 × 10 –9) = W + K 2
–34
460 × 10
4.32 × 10 = W + 2K ------ (2)
–19
1
(1) × 2 – (2):
2.65 × 10 × 2 – 4.32 × 10 = (2W – W) + (2K – 2K )
-19
–19
1
1
W = 9.80 × 10 J
-20
242 LS 7.3.4