Page 114 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 114
Chapter 3 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL CARDIAC AND VASCULAR NEEDS 99
Patients who cannot tolerate exercise may be stressed with drug-induced
alternatives, which will also increase the oxygen demands and workload to the
heart. Examples of pharmacological agents include adenosine, dipyridamole, or
dobutamine.
Whichever stress test modalities are used, visual imaging will identify isch-
emic dysfunctions of the myocardium. Such results may indicate a need for
further care such as a cardiac catheterization to determine the patency of the
coronary arteries. Balloon angioplasty, arterial stent insertion, or even coronary
artery bypass surgery might be further recommended.
Pulmonary Artery Catheter (PAC)
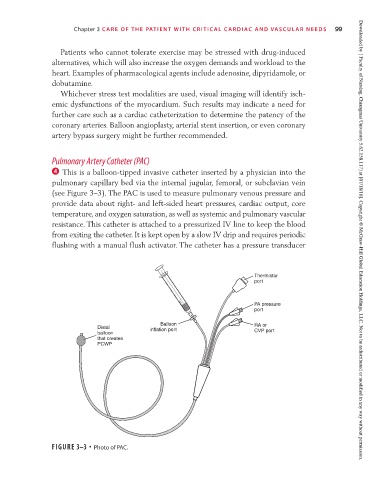
4 This is a balloon-tipped invasive catheter inserted by a physician into the
pulmonary capillary bed via the internal jugular, femoral, or subclavian vein
(see Figure 3–3). The PAC is used to measure pulmonary venous pressure and
provide data about right- and left-sided heart pressures, cardiac output, core
temperature, and oxygen saturation, as well as systemic and pulmonary vascular
resistance. This catheter is attached to a pressurized IV line to keep the blood
from exiting the catheter. It is kept open by a slow IV drip and requires periodic
flushing with a manual flush activator. The catheter has a pressure transducer Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Thermistor
port
PA pressure
port
Balloon RA or
Distal inflation port
balloon CVP port
that creates
PCWP
FIGURE 3–3 • Photo of PAC.