Page 136 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 136
Chapter 3 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL CARDIAC AND VASCULAR NEEDS 121
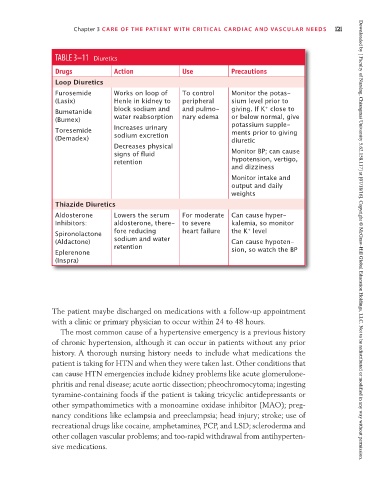
TABLE 3–11 Diuretics
Drugs Action Use Precautions
Loop Diuretics
Furosemide Works on loop of To control Monitor the potas-
(Lasix) Henle in kidney to peripheral sium level prior to
+
Bumetanide block sodium and and pulmo- giving. If K close to
(Bumex) water reabsorption nary edema or below normal, give
potassium supple-
Toresemide Increases urinary ments prior to giving
(Demadex) sodium excretion diuretic
Decreases physical
signs of fluid Monitor BP; can cause
retention hypotension, vertigo,
and dizziness
Monitor intake and
output and daily
weights
Thiazide Diuretics
Aldosterone Lowers the serum For moderate Can cause hyper-
Inhibitors: aldosterone, there- to severe kalemia, so monitor
+
Spironolactone fore reducing heart failure the K level
(Aldactone) sodium and water Can cause hypoten- Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
retention
Eplerenone sion, so watch the BP
(Inspra)
The patient maybe discharged on medications with a follow-up appointment
with a clinic or primary physician to occur within 24 to 48 hours.
The most common cause of a hypertensive emergency is a previous history
of chronic hypertension, although it can occur in patients without any prior
history. A thorough nursing history needs to include what medications the
patient is taking for HTN and when they were taken last. Other conditions that
can cause HTN emergencies include kidney problems like acute glomerulone-
phritis and renal disease; acute aortic dissection; pheochromocytoma; ingesting
tyramine-containing foods if the patient is taking tricyclic antidepressants or
other sympathomimetics with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAO); preg-
nancy conditions like eclampsia and preeclampsia; head injury; stroke; use of
recreational drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, PCP, and LSD; scleroderma and
other collagen vascular problems; and too-rapid withdrawal from antihyperten-
sive medications.