Page 184 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 184
Chapter 4 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL CARDIAC RHY THM DISTURBANCE NEEDS 169
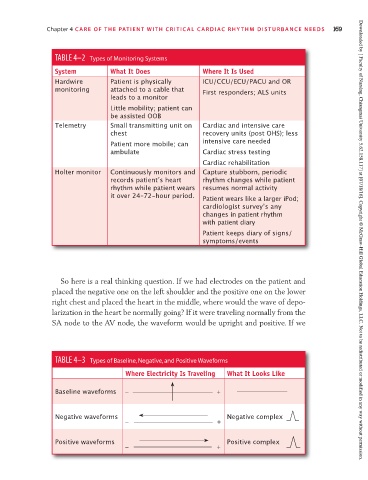
TABLE 4–2 Types of Monitoring Systems
System What It Does Where It Is Used
Hardwire Patient is physically ICU/CCU/ECU/PACU and OR
monitoring attached to a cable that First responders; ALS units
leads to a monitor
Little mobility; patient can
be assisted OOB
Telemetry Small transmitting unit on Cardiac and intensive care
chest recovery units (post OHS); less
Patient more mobile; can intensive care needed
ambulate Cardiac stress testing
Cardiac rehabilitation
Holter monitor Continuously monitors and Capture stubborn, periodic
records patientʼs heart rhythm changes while patient
rhythm while patient wears resumes normal activity
it over 24–72-hour period. Patient wears like a larger iPod;
cardiologist surveyʼs any
changes in patient rhythm
with patient diary
Patient keeps diary of signs/
symptoms/events Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
So here is a real thinking question. If we had electrodes on the patient and
placed the negative one on the left shoulder and the positive one on the lower
right chest and placed the heart in the middle, where would the wave of depo-
larization in the heart be normally going? If it were traveling normally from the
SA node to the AV node, the waveform would be upright and positive. If we
TABLE 4–3 Types of Baseline, Negative, and Positive Waveforms
Where Electricity Is Traveling What It Looks Like
Baseline waveforms − +
Negative waveforms Negative complex
− +
Positive waveforms Positive complex
− +