Page 331 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 331
316 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
noted that GH levels tend to increase during sleep, but the reasons are unknown.
Severe malnutrition also creates a prolonged elevation of GH.
An MRI will determine the extension of a pituitary tumor into surrounding
tissue, while a CAT scan with contrast dye will help to localize a pituitary tumor.
A complete ophthalmologic examination is also indicated due to potential
increased pressure occurring over the optic nerves.
Treatment
Someone with a pituitary tumor may undergo radiation or surgery to remove
the tumor. The surgical term is hypophysectomy and is accomplished using the
transsphenoidal approach. An incision is made in the inner aspect of the upper
lip and gingiva and the sella turcica is entered through the floor of the nose and
sphenoid sinuses.
Radiation is indicated when surgery fails to produce successful results. It has
also been used to reduce the size of a tumor prior to surgery. Gamma surgery
or stereotactic radiosurgery can be used to treat small, inaccessible pituitary
tumors. Radiation is delivered to a single site from multiple angles. It occludes
the blood vessels feeding the tumor, which starves the tumor.
Drug Therapy to Decrease GH Levels Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
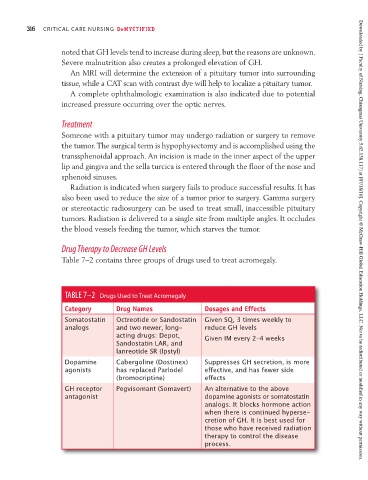
Table 7–2 contains three groups of drugs used to treat acromegaly.
TABLE 7–2 Drugs Used to Treat Acromegaly
Category Drug Names Dosages and Effects
Somatostatin Octreotide or Sandostatin Given SQ, 3 times weekly to
analogs and two newer, long- reduce GH levels
acting drugs: Depot, Given IM every 2–4 weeks
Sandostatin LAR, and
lanreotide SR (Ipstyl)
Dopamine Cabergoline (Dostinex) Suppresses GH secretion, is more
agonists has replaced Parlodel effective, and has fewer side
(bromocriptine) effects
GH receptor Pegvisomant (Somavert) An alternative to the above
antagonist dopamine agonists or somatostatin
analogs. It blocks hormone action
when there is continued hyperse-
cretion of GH. It is best used for
those who have received radiation
therapy to control the disease
process.