Page 338 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 338
Chapter 7 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS 323
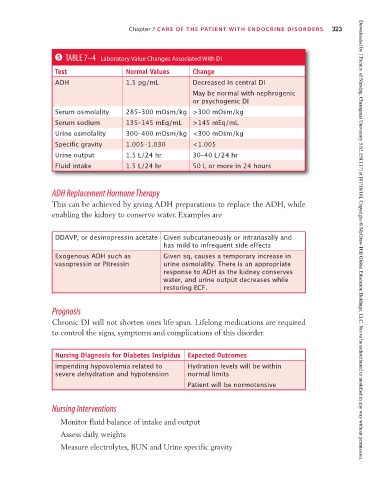
5 TABLE 7–4 Laboratory Value Changes Associated With DI
Test Normal Values Change
ADH 1.5 pg/mL Decreased in central DI
May be normal with nephrogenic
or psychogenic DI
Serum osmolality 285–300 mOsm/kg >300 mOsm/kg
Serum sodium 135–145 mEq/mL >145 mEq/mL
Urine osmolality 300–400 mOsm/kg <300 mOsm/kg
Specific gravity 1.005–1.030 <1.005
Urine output 1.5 L/24 hr 30–40 L/24 hr
Fluid intake 1.5 L/24 hr 50 L or more in 24 hours
ADH Replacement Hormone Therapy
This can be achieved by giving ADH preparations to replace the ADH, while
enabling the kidney to conserve water. Examples are
DDAVP, or desmopressin acetate Given subcutaneously or intranasally and
has mild to infrequent side effects Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Exogenous ADH such as Given sq, causes a temporary increase in
vasopressin or Pitressin urine osmolality. There is an appropriate
response to ADH as the kidney conserves
water, and urine output decreases while
restoring ECF.
Prognosis
Chronic DI will not shorten ones life span. Lifelong medications are required
to control the signs, symptoms and complications of this disorder.
Nursing Diagnosis for Diabetes Insipidus Expected Outcomes
Impending hypovolemia related to Hydration levels will be within
severe dehydration and hypotension normal limits
Patient will be normotensive
Nursing Interventions
Monitor fluid balance of intake and output
Assess daily weights
Measure electrolytes, BUN and Urine specific gravity