Page 176 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 176
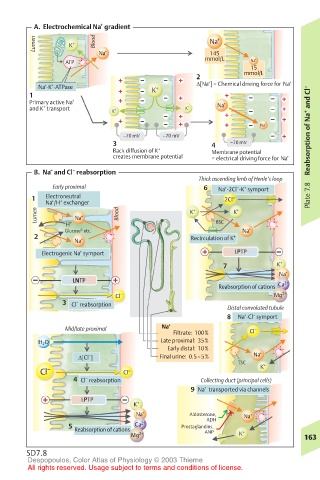
A. Electrochemical Na gradient
+
Lumen K + Blood Na +
Na + 145
ATP mmol/L Na +
15
mmol/L
2
+
+
+
Na -K -ATPase K + ∆[Na ] = Chemical driving force for Na +
1
Primary active Na + Na +
+
and K transport K + K +
Na +
–70 mV –70 mV Reabsorption of Na + and Cl –
3 4 –70 mV
Back diffusion of K + Membrane potential
creates membrane potential = electrical driving force for Na +
+
–
B. Na and Cl reabsorption
Thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop
Early proximal 6 Na -2Cl -K symport
–
+
+
1 Electroneutral 2Cl – Plate 7.8
+
+
Na /H exchanger
Lumen + Na + Blood K + BSC K +
H
Glucose 0 etc. Na +
2 Recirculation of K +
Na +
Electrogenic Na symport LPTP
+
7 K +
Na +
LNTP 2+
Reabsorption of cations Ca
Cl – Mg 2+
–
3 Cl reabsorption
Distal convoluted tubule
–
8 Na -Cl symport
+
Mid/late proximal Na + –
Filtrate: 100% Cl
H 2 O Late proximal: 35%
Early distal: 10%
–
∆[Cl ] Final urine: 0.5–5% Na +
TSC +
Cl – Cl – K
–
4 Cl reabsorption Collecting duct (principal cells)
+
9 Na transported via channels
LPTP
K +
Na + Aldosterone, Na +
ADH
5 Reabsorption of cations Ca 2+ Prostaglandins,
Mg 2+ ANP K + 163
SD7.8
SD7.8
SD7.8SD7.8
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.