Page 224 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 224
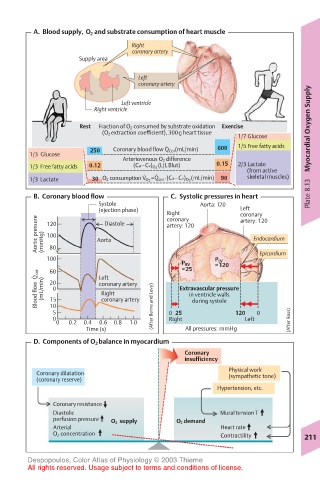
A. Blood supply, O 2 and substrate consumption of heart muscle
Right
coronary artery
Supply area
Left
coronary artery
Left ventricle
Right ventricle Oxygen Supply
Rest Fraction of O 2 consumed by substrate oxidation Exercise
(O 2 extraction coefficient), 300g heart tissue
1/7 Glucose
·
250 Coronary blood flow Q Cor (mL/min) 600 1/5 Free fatty acids
1/3 Glucose Myocardial
Arteriovenous O 2 difference
1/3 Free fatty acids 0.12 (Ca–Cv) O 2 (L/L Blut) 0.15 2/3 Lactate
(from active
·
·
1/3 Lactate 30 O 2 consumption V O 2 =Q cor ·(Ca–Cv) O 2 (mL/min) 90 skeletal muscles)
B. Coronary blood flow C. Systolic pressures in heart Plate 8.13
Systole Aorta: 120
(ejection phase) Right Left
coronary
coronary
Aortic pressure (mmHg) 120 Aorta artery: 120 Endocardium
artery: 120
Diastole
100
80
100 P LV Epicardium
P RV =120
=25
Q cor 60 Left
Blood flow · (mL/min) 15 0 Right Extravascular pressure
20
coronary artery
in ventricle walls
coronary artery
during systole
10
5 (After Berne and Levy) 0 25 120 0
0 Right Left
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 (After Ross)
Time (s) All pressures: mmHg
D. Components of O 2 balance in myocardium
Coronary
insufficiency
Physical work
Coronary dilatation (sympathetic tone)
(coronary reserve)
Hypertension, etc.
Coronary resistance
Diastolic Mural tension T
perfusion pressure O 2 supply O 2 demand
Arterial Heart rate
O 2 concentration Contractility 211
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.