Page 52 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 52
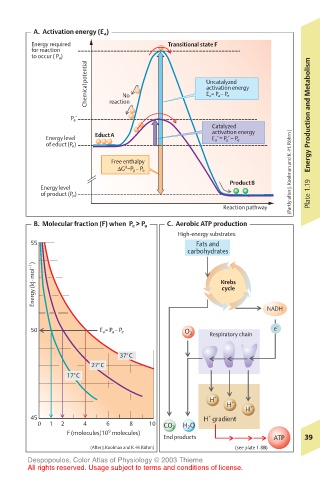
A. Activation energy (E a )
Energy required Transitional state F
for reaction
to occur ( P a )
Chemical potential No Uncatalyzed
activation energy
E a = P a – P e
P a ´ reaction Energy Production and Metabolism
Catalyzed
activation energy
Energy level EductA E a ´= P a ´– P e
of educt (P e )
Free enthalpy
0
∆G =P p – P e (Partly after J. Koolman and K.-H. Röhm )
ProductB
Energy level
of product (P p ) Plate 1.19
Reaction pathway
B. Molecular fraction (F) when P e > P a C. Aerobic ATP production
High-energy substrates:
55 Fats and
carbohydrates
Energy (kJ·mol –1 ) Krebs
cycle
NADH
50 E a = P a – P e O 2 Respiratory chain e –
37°C
27°C
17°C
H + +
H +
H
+
45 H gradient
0 1 2 4 6 8 10 CO 2 H 2 O
9
F (molecules/10 molecules)
39
End products ATP 39
(After J.Koolman and K.-H.Röhm) (see plate 1.8B)
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.