Page 50 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 50
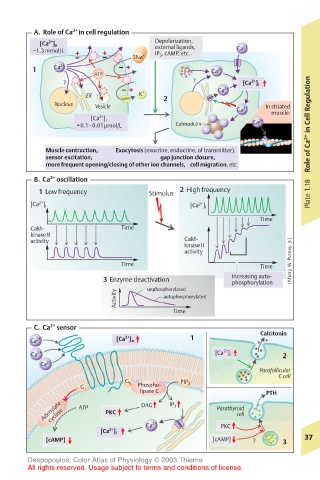
A. Role of Ca in cell regulation
2+
2+ Depolarization,
[Ca ] o external ligands, 2 2+ +
=1.3mmol/L IP 3 , cAMP, etc.. C Ca a
3Na +
1 Ca 2+ Ca 2+
ATP
2+
? ? [Ca ] i
Ca 2+
ER K + 2
Nucleus Vesicle Ca 2+ In striated
2+ muscle:
[Ca ] i Ca 2+
=0.1–0.01µmol/L Calmodulin Role of Ca 2+ in Cell Regulation
Muscle contraction, Exocytosis (exocrine, endocrine, of transmitter), Troponin
sensor excitation, gap junction closure,
more frequent opening/closing of other ion channels, cell migration, etc.
2+
B. Ca oscillation
1 Low frequency Stimulus 2 High frequency Plate 1.18
2+ 2+
[Ca ] i [Ca ] i
Time
CaM- Time
kinase II
activity CaM-
kinase II
activity
Time Time (After J. W. Putney, Jr.)
3 Enzyme deactivation Increasing auto-
phosphorylation
unphosphorylated
Activity autophosphorylated
Time
2+
C. Ca sensor Calcitonin
2+
Ca 2+ [Ca ] o 1
2+
Ca 2+ [Ca ] i 2
Ca 2+
Parafollicular
C cell
G q Phospho- PIP 2
G i
lipase C PTH
Adenylate ATP PKC DAG IP 3 Parathyroid
cyclase
cell
Ca 2+ PKC
2+
[Ca ] i
37
[cAMP] [cAMP] ? 3 37
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.