Page 268 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 268
ECA4 7/18/06 6:48 PM Page 253
Course and distribution of nerves 253
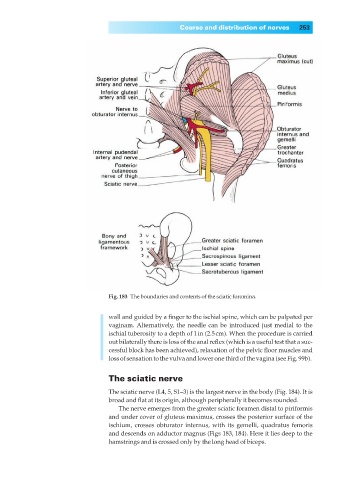
Fig. 183◊The boundaries and contents of the sciatic foramina.
wall and guided by a finger to the ischial spine, which can be palpated per
vaginam. Alternatively, the needle can be introduced just medial to the
ischial tuberosity to a depth of 1in (2.5cm). When the procedure is carried
out bilaterally there is loss of the anal reflex (which is a useful test that a suc-
cessful block has been achieved), relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles and
loss of sensation to the vulva and lower one third of the vagina (see Fig. 99b).
The sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve (L4, 5, S1–3) is the largest nerve in the body (Fig. 184). It is
broad and flat at its origin, although peripherally it becomes rounded.
The nerve emerges from the greater sciatic foramen distal to piriformis
and under cover of gluteus maximus, crosses the posterior surface of the
ischium, crosses obturator internus, with its gemelli, quadratus femoris
and descends on adductor magnus (Figs 183, 184). Here it lies deep to the
hamstrings and is crossed only by the long head of biceps.