Page 376 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 376
ECA6 7/18/06 6:54 PM Page 361
The brain 361
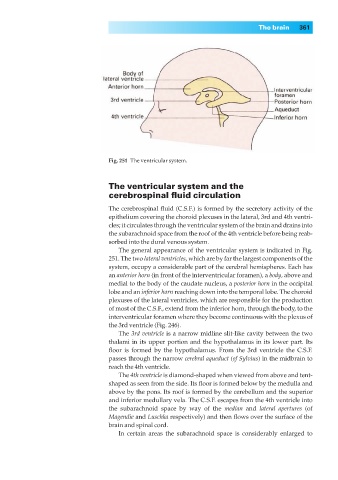
Fig. 251◊The ventricular system.
The ventricular system and the
cerebrospinal fluid circulation
The cerebrospinal fluid (C.S.F.) is formed by the secretory activity of the
epithelium covering the choroid plexuses in the lateral, 3rd and 4th ventri-
cles; it circulates through the ventricular system of the brain and drains into
the subarachnoid space from the roof of the 4th ventricle before being reab-
sorbed into the dural venous system.
The general appearance of the ventricular system is indicated in Fig.
251. The two lateral ventricles, which are by far the largest components of the
system, occupy a considerable part of the cerebral hemispheres. Each has
an anterior horn (in front of the interventricular foramen), a body, above and
medial to the body of the caudate nucleus, a posterior horn in the occipital
lobe and an inferior horn reaching down into the temporal lobe. The choroid
plexuses of the lateral ventricles, which are responsible for the production
of most of the C.S.F., extend from the inferior horn, through the body, to the
interventricular foramen where they become continuous with the plexus of
the 3rd ventricle (Fig. 246).
The 3rd ventricle is a narrow midline slit-like cavity between the two
thalami in its upper portion and the hypothalamus in its lower part. Its
floor is formed by the hypothalamus. From the 3rd ventricle the C.S.F.
passes through the narrow cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius) in the midbrain to
reach the 4th ventricle.
The 4th ventricle is diamond-shaped when viewed from above and tent-
shaped as seen from the side. Its floor is formed below by the medulla and
above by the pons. Its roof is formed by the cerebellum and the superior
and inferior medullary vela. The C.S.F. escapes from the 4th ventricle into
the subarachnoid space by way of the median and lateral apertures (of
Magendie and Luschka respectively) and then flows over the surface of the
brain and spinal cord.
In certain areas the subarachnoid space is considerably enlarged to