Page 10 - Critical Care Notes
P. 10
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 4
BASICS
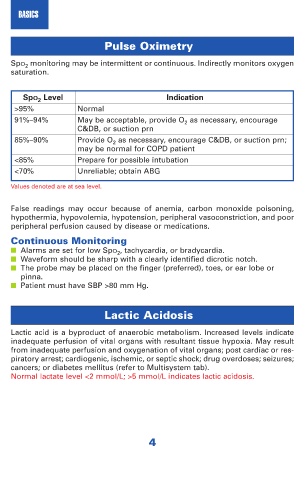
Pulse Oximetry
SpO 2 monitoring may be intermittent or continuous. Indirectly monitors oxygen
saturation.
SpO 2 Level Indication
>95% Normal
91%–94% May be acceptable, provide O 2 as necessary, encourage
C&DB, or suction prn
85%–90% Provide O 2 as necessary, encourage C&DB, or suction prn;
may be normal for COPD patient
<85% Prepare for possible intubation
<70% Unreliable; obtain ABG
Values denoted are at sea level.
False readings may occur because of anemia, carbon monoxide poisoning,
hypothermia, hypovolemia, hypotension, peripheral vasoconstriction, and poor
peripheral perfusion caused by disease or medications.
Continuous Monitoring
■ Alarms are set for low SpO 2 , tachycardia, or bradycardia.
■ Waveform should be sharp with a clearly identified dicrotic notch.
■ The probe may be placed on the finger (preferred), toes, or ear lobe or
pinna.
■ Patient must have SBP >80 mm Hg.
Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acid is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism. Increased levels indicate
inadequate perfusion of vital organs with resultant tissue hypoxia. May result
from inadequate perfusion and oxygenation of vital organs; post cardiac or res-
piratory arrest; cardiogenic, ischemic, or septic shock; drug overdoses; seizures;
cancers; or diabetes mellitus (refer to Multisystem tab).
Normal lactate level <2 mmol/L; >5 mmol/L indicates lactic acidosis.
4