Page 11 - Critical Care Notes
P. 11
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 5
5
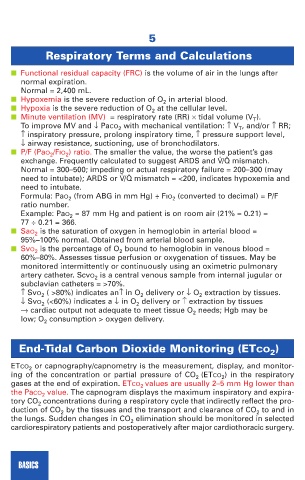
Respiratory Terms and Calculations
■ Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air in the lungs after
normal expiration.
Normal = 2,400 mL.
■ Hypoxemia is the severe reduction of O 2 in arterial blood.
■ Hypoxia is the severe reduction of O 2 at the cellular level.
■ Minute ventilation (MV) = respiratory rate (RR) × tidal volume (V T ).
To improve MV and ↓ PaCO 2 with mechanical ventilation: ↑ V T , and/or ↑ RR;
↑ inspiratory pressure, prolong inspiratory time, ↑ pressure support level,
↓ airway resistance, suctioning, use of bronchodilators.
■ P/F (PaO 2 /FIO 2 ) ratio. The smaller the value, the worse the patient’s gas
· ·
exchange. Frequently calculated to suggest ARDS and V/Q mismatch.
Normal = 300–500; impeding or actual respiratory failure = 200–300 (may
· ·
need to intubate); ARDS or V/Q mismatch = <200, indicates hypoxemia and
need to intubate.
Formula: PaO 2 (from ABG in mm Hg) ÷ FIO 2 (converted to decimal) = P/F
ratio number.
Example: PaO 2 = 87 mm Hg and patient is on room air (21% = 0.21) =
77 ÷ 0.21 = 366.
■ SaO 2 is the saturation of oxygen in hemoglobin in arterial blood =
95%–100% normal. Obtained from arterial blood sample.
■ SvO 2 is the percentage of O 2 bound to hemoglobin in venous blood =
60%–80%. Assesses tissue perfusion or oxygenation of tissues. May be
monitored intermittently or continuously using an oximetric pulmonary
artery catheter. ScvO 2 is a central venous sample from internal jugular or
subclavian catheters = >70%.
↑ SvO 2 ( >80%) indicates an↑ in O 2 delivery or ↓ O 2 extraction by tissues.
↓ SvO 2 (<60%) indicates a ↓ in O 2 delivery or ↑ extraction by tissues
→ cardiac output not adequate to meet tissue O 2 needs; Hgb may be
low; O 2 consumption > oxygen delivery.
End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring (ETCO )
2
ETCO 2 or capnography/capnometry is the measurement, display, and monitor-
ing of the concentration or partial pressure of CO 2 (ETCO 2 ) in the respiratory
gases at the end of expiration. ETCO 2 values are usually 2–5 mm Hg lower than
the PaCO 2 value. The capnogram displays the maximum inspiratory and expira-
tory CO 2 concentrations during a respiratory cycle that indirectly reflect the pro-
duction of CO 2 by the tissues and the transport and clearance of CO 2 to and in
the lungs. Sudden changes in CO 2 elimination should be monitored in selected
cardiorespiratory patients and postoperatively after major cardiothoracic surgery.
BASICS