Page 12 - Critical Care Notes
P. 12
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 6
BASICS
ETCO 2 monitoring can also be used to verify ETT position, assess readiness for
extubation, and monitor the effectiveness of CPR and predict patient survival.
ETCO 2 <10 mm Hg after 20 min CPR indicates poor outcome. It is sometimes
referred to as the “ventilation vital sign.”
Causes of ↑ ETCO 2 Causes of ↓ ETCO 2
Fever Hypothermia
Hypertension Hypotension and shock
Increased cardiac output Cardiac perfusion changes
Respiratory compromise Decreased cardiac output, heart failure
Hypoventilation Cardiac arrest and apnea
Airway obstruction Hyperventilation
Bronchial intubation Airway obstruction
Hypovolemia Accidental extubation
Sepsis Pulmonary embolus
Seizures Hypervolemia
Normal range of ETCO 2 is 35–45 mm Hg. CO 2 and ETCO 2 should correlate with-
in 2–5 mm Hg.
↑ RR (hyperventilation) → ↓ CO 2 → ETCO 2 < 35 = respiratory alkalosis
↓ RR (hypoventilation) →↑ CO 2 → ETCO 2 > 45 = respiratory acidosis
Five characteristics of the capnogram should be evaluated: frequency, rhythm,
height, baseline, and shape. Also note changes if patient is disconnected from ven-
tilator and attempts of spontaneous breaths if patient is receiving paralytic agents.
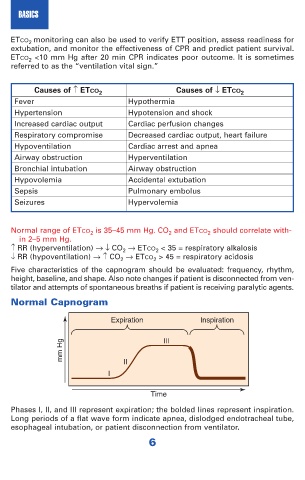
Normal Capnogram
Expiration Inspiration
mm Hg II III
I
Time
Phases I, II, and III represent expiration; the bolded lines represent inspiration.
Long periods of a flat wave form indicate apnea, dislodged endotracheal tube,
esophageal intubation, or patient disconnection from ventilator.
6