Page 37 - Critical Care Notes
P. 37
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 31
31
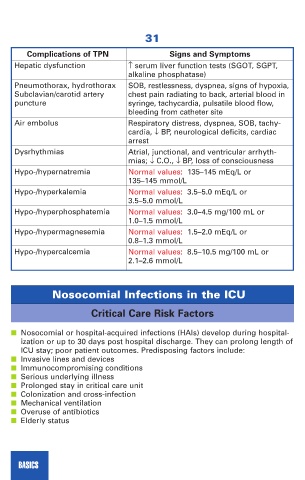
Complications of TPN Signs and Symptoms
Hepatic dysfunction ↑ serum liver function tests (SGOT, SGPT,
alkaline phosphatase)
Pneumothorax, hydrothorax SOB, restlessness, dyspnea, signs of hypoxia,
Subclavian/carotid artery chest pain radiating to back, arterial blood in
puncture syringe, tachycardia, pulsatile blood flow,
bleeding from catheter site
Air embolus Respiratory distress, dyspnea, SOB, tachy-
cardia, ↓ BP, neurological deficits, cardiac
arrest
Dysrhythmias Atrial, junctional, and ventricular arrhyth-
mias; ↓ C.O., ↓ BP, loss of consciousness
Hypo-/hypernatremia Normal values: 135–145 mEq/L or
135–145 mmol/L
Hypo-/hyperkalemia Normal values: 3.5–5.0 mEq/L or
3.5–5.0 mmol/L
Hypo-/hyperphosphatemia Normal values: 3.0–4.5 mg/100 mL or
1.0–1.5 mmol/L
Hypo-/hypermagnesemia Normal values: 1.5–2.0 mEq/L or
0.8–1.3 mmol/L
Hypo-/hypercalcemia Normal values: 8.5–10.5 mg/100 mL or
2.1–2.6 mmol/L
Nosocomial Infections in the ICU
Critical Care Risk Factors
■ Nosocomial or hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) develop during hospital-
ization or up to 30 days post hospital discharge. They can prolong length of
ICU stay; poor patient outcomes. Predisposing factors include:
■ Invasive lines and devices
■ Immunocompromising conditions
■ Serious underlying illness
■ Prolonged stay in critical care unit
■ Colonization and cross-infection
■ Mechanical ventilation
■ Overuse of antibiotics
■ Elderly status
BASICS