Page 249 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 249
Initiation of Mechanical Ventilation 215
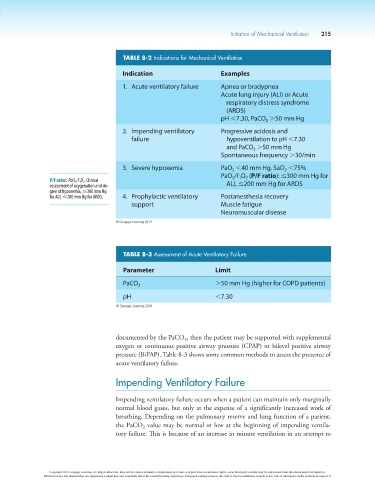
TABLE 8-2 Indications for Mechanical Ventilation
Indication Examples
1. Acute ventilatory failure Apnea or bradypnea
Acute lung injury (ALI) or Acute
respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS)
pH ,7.30, PaCO .50 mm Hg
2
2. Impending ventilatory Progressive acidosis and
failure hypoventilation to pH ,7.30
and PaCO .50 mm Hg
2
Spontaneous frequency .30/min
3. Severe hypoxemia PaO ,40 mm Hg, SaO ,75%
2
2
PaO /F O (P/F ratio): ≤300 mm Hg for
P/F ratio: PaO 2 / F I O 2 . Clinical 2 I 2
assessment of oxygenation and de- ALI, ≤200 mm Hg for ARDS
gree of hypoxemia, ≤300 mm Hg
for ALI, ≤200 mm Hg for ARDS. 4. Prophylactic ventilatory Postanesthesia recovery
support Muscle fatigue
Neuromuscular disease
© Cengage Learning 2014
TABLE 8-3 Assessment of Acute Ventilatory Failure
Parameter Limit
PaCO 2 .50 mm Hg (higher for COPD patients)
pH ,7.30
© Cengage Learning 2014
documented by the PaCO , then the patient may be supported with supplemental
2
oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or bilevel positive airway
pressure (BiPAP). Table 8-3 shows some common methods to assess the presence of
acute ventilatory failure.
Impending Ventilatory Failure
Impending ventilatory failure occurs when a patient can maintain only marginally
normal blood gases, but only at the expense of a significantly increased work of
breathing. Depending on the pulmonary reserve and lung function of a patient,
the PaCO value may be normal or low at the beginning of impending ventila-
2
tory failure. This is because of an increase in minute ventilation in an attempt to
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.