Page 680 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 680
646 Chapter 19
Over the next 24 hours, her condition quickly deteriorated, requiring 100% F O
I
2
and increasing levels of PEEP to maintain adequate oxygenation.
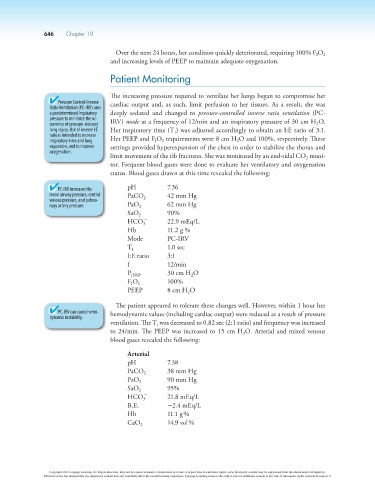
Patient Monitoring
The increasing pressure required to ventilate her lungs began to compromise her
Pressure Control-Inverse cardiac output and, as such, limit perfusion to her tissues. As a result, she was
Ratio Ventilation (PC-IRV) uses
a predetermined inspiratory deeply sedated and changed to pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation (PC-
pressure to minimize the oc-
2
currence of pressure-induced IRV) mode at a frequency of 12/min and an inspiratory pressure of 30 cm H O.
lung injury. Use of inverse I:E Her inspiratory time (T ) was adjusted accordingly to obtain an I:E ratio of 3:1.
ratio is intended to increase I
inspiratory time and lung Her PEEP and F O requirements were 8 cm H O and 100%, respectively. These
I
2
2
expansion, and to improve settings provided hyperexpansion of the chest in order to stabilize the thorax and
oxygenation.
limit movement of the rib fractures. She was monitored by an end-tidal CO moni-
2
tor. Frequent blood gases were done to evaluate her ventilatory and oxygenation
status. Blood gases drawn at this time revealed the following:
PC-IRV increases the pH 7.36
mean airway pressure, central PaCO 42 mm Hg
venous pressure, and pulmo- 2
nary artery pressure. PaO 2 62 mm Hg
SaO 2 90%
-
HCO 22.9 mEq/L
3
Hb 11.2 g %
Mode PC-IRV
T I 1.0 sec
I:E ratio 3:1
f 12/min
P INSP 30 cm H O
2
F O 2 100%
I
PEEP 8 cm H O
2
The patient appeared to tolerate these changes well. However, within 1 hour her
PC-IRV can cause hemo- hemodynamic values (including cardiac output) were reduced as a result of pressure
dynamic instability.
ventilation. The T was decreased to 0.82 sec (2:1 ratio) and frequency was increased
I
to 24/min. The PEEP was increased to 15 cm H O. Arterial and mixed venous
2
blood gases revealed the following:
Arterial
pH 7.38
PaCO 2 38 mm Hg
PaO 2 90 mm Hg
SaO 2 95%
-
HCO 21.8 mEq/L
3
B.E. 22.4 mEq/L
Hb 11.1 g %
CaO 2 14.9 vol %
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.