Page 688 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 688
654 Chapter 19
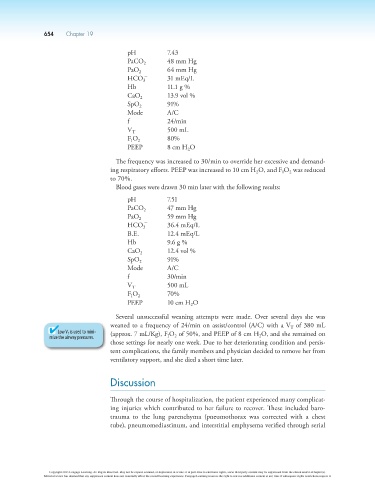
pH 7.43
PaCO 2 48 mm Hg
PaO 2 64 mm Hg
-
HCO 31 mEq/L
3
Hb 11.1 g %
CaO 2 13.9 vol %
SpO 2 91%
Mode A/C
f 24/min
V T 500 mL
F O 2 80%
I
PEEP 8 cm H O
2
The frequency was increased to 30/min to override her excessive and demand-
ing respiratory efforts. PEEP was increased to 10 cm H O, and F O was reduced
2
2
I
to 70%.
Blood gases were drawn 30 min later with the following results:
pH 7.51
PaCO 2 47 mm Hg
PaO 2 59 mm Hg
-
HCO 36.4 mEq/L
3
B.E. 12.4 mEq/L
Hb 9.6 g %
CaO 2 12.4 vol %
SpO 2 91%
Mode A/C
f 30/min
V T 500 mL
F O 2 70%
I
PEEP 10 cm H O
2
Several unsuccessful weaning attempts were made. Over several days she was
weaned to a frequency of 24/min on assist/control (A/C) with a V of 380 mL
T
Low V T is used to mini- (approx. 7 mL/Kg), F O of 50%, and PEEP of 8 cm H O, and she remained on
mize the airway pressures. I 2 2
those settings for nearly one week. Due to her deteriorating condition and persis-
tent complications, the family members and physician decided to remove her from
ventilatory support, and she died a short time later.
Discussion
Through the course of hospitalization, the patient experienced many complicat-
ing injuries which contributed to her failure to recover. These included baro-
trauma to the lung parenchyma (pneumothorax was corrected with a chest
tube), pneumomediastinum, and interstitial emphysema verified through serial
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.