Page 622 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 622
009
009
0/2
6/3
0/2
7:4
5
7:4
1
1
6/3
q
q
q
22.
22.
0
0
0
xd
xd
p
p
A
A
A
ara
ara
t
p
t
98
Pa
g
Pa
5
Pa
e 5
98
e 5
g
g
LWBK340-c25_
LWB
LWB K34 0-c 25_ p pp595-622.qxd 06/30/2009 17:45 Page 598 Aptara
25_
0-c
K34
59
5-6
5-6
p
59
598 PA R T I V / Pathophysiology and Management of Heart Disease
C
B
D
A
E
F
G
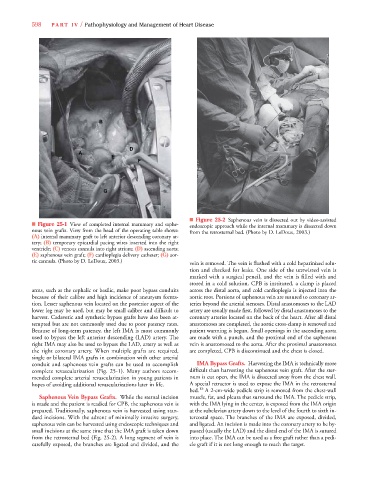
■ Figure 25-2 Saphenous vein is dissected out by video-assisted
■ Figure 25-1 View of completed internal mammary and saphe- endoscopic approach while the internal mammary is dissected down
nous vein grafts. View from the head of the operating table shows: from the retrosternal bed. (Photo by D. LeDoux, 2003.)
(A) internal mammary graft to left anterior descending coronary ar-
tery; (B) temporary epicardial pacing wires inserted into the right
ventricle; (C) venous cannula into right atrium; (D) ascending aorta;
(E) saphenous vein graft; (F) cardioplegia delivery catheter; (G) aor-
tic cannula. (Photo by D. LeDoux, 2003.) vein is removed. The vein is flushed with a cold heparinized solu-
tion and checked for leaks. One side of the untwisted vein is
marked with a surgical pencil, and the vein is filled with and
stored in a cold solution. CPB is instituted, a clamp is placed
arms, such as the cephalic or basilic, make poor bypass conduits across the distal aorta, and cold cardioplegia is injected into the
because of their calibre and high incidence of aneurysm forma- aortic root. Portions of saphenous vein are sutured to coronary ar-
tion. Lesser saphenous vein located on the posterior aspect of the teries beyond the arterial stenoses. Distal anastomoses to the LAD
lower leg may be used, but may be small calibre and difficult to artery are usually made first, followed by distal anastomoses to the
harvest. Cadaveric and synthetic bypass grafts have also been at- coronary arteries located on the back of the heart. After all distal
tempted but are not commonly used due to poor patency rates. anastomoses are completed, the aortic cross-clamp is removed and
Because of long-term patency, the left IMA is most commonly patient warming is begun. Small openings in the ascending aorta
used to bypass the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. The are made with a punch, and the proximal end of the saphenous
right IMA may also be used to bypass the LAD, artery as well as vein is anastomosed to the aorta. After the proximal anastomoses
the right coronary artery. When multiple grafts are required, are completed, CPB is discontinued and the chest is closed.
single or bilateral IMA grafts in combination with other arterial
conduit and saphenous vein grafts can be used to accomplish IMA Bypass Grafts. Harvesting the IMA is technically more
complete revascularization (Fig. 25-1). Many authors recom- difficult than harvesting the saphenous vein graft. After the ster-
mended complete arterial revascularization in young patients in num is cut open, the IMA is dissected away from the chest wall.
hopes of avoiding additional revascularizations later in life. A special retractor is used to expose the IMA in the retrosternal
13
bed. A 2-cm-wide pedicle strip is removed from the chest-wall
Saphenous Vein Bypass Grafts. While the sternal incision muscle, fat, and pleura that surround the IMA. The pedicle strip,
is made and the patient is readied for CPB, the saphenous vein is with the IMA lying in the center, is exposed from the IMA origin
prepared. Traditionally, saphenous vein is harvested using stan- at the subclavian artery down to the level of the fourth to sixth in-
dard incisions. With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, tercostal space. The branches of the IMA are exposed, divided,
saphenous vein can be harvested using endoscopic techniques and and ligated. An incision is made into the coronary artery to be by-
small incisions at the same time that the IMA graft is taken down passed (usually the LAD) and the distal end of the IMA is sutured
from the retrosternal bed (Fig. 25-2). A long segment of vein is into place. The IMA can be used as a free graft rather than a pedi-
carefully exposed, the branches are ligated and divided, and the cle graft if it is not long enough to reach the target.