Page 627 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 627
LWBK340-c25_p595-622.qxd 06/30/2009 17:45 Page 603 Aptara
C HAPTER 2 5 / Cardiac Surgery 603
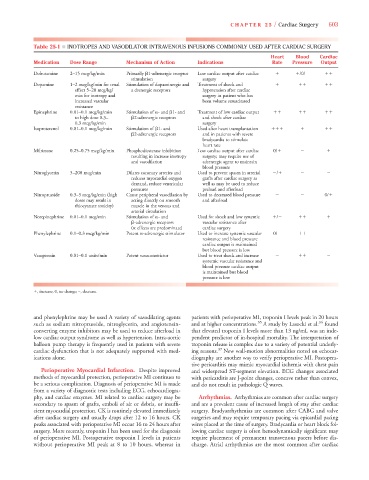
Table 25-1 ■ INOTROPES AND VASODILATOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSIONS COMMONLY USED AFTER CARDIAC SURGERY
Heart Blood Cardiac
Medication Dose Range Mechanism of Action Indications Rate Pressure Output
Dobutamine 2–15 mcg/kg/min Primarily 1-adrenergic receptor Low cardiac output after cardiac
/0/
stimulation surgery
Dopamine 1–2 mcg/kg/min for renal Stimulation of dopaminergic and Treatment of shock and
effect 5–20 mcg/kg/ a drenergic receptors hypotension after cardiac
min for inotropy and surgery in patient who has
increased vascular been volume resuscitated
resistance
Epinephrine 0.01–0.1 mcg/kg/min Stimulation of - and 1- and Treatment of low cardiac output
to high dose 0.3– 2-adrenergic receptors and shock after cardiac
0.3 mcg/kg/min surgery
Isoproterenol 0.01–0.1 mcg/kg/min Stimulation of 1- and Used after heart transplantation
2-adrenergic receptors and in patients with severe
bradycardia to stimulate
heart rate
Milrinone 0.25–0.75 mcg/kg/min Phosphodiesterase inhibition Low cardiac output after cardiac 0/
resulting in increase inotropy surgery; may require use of
and vasodilation adrenergic agent to maintain
blood pressure
Nitroglycerin 5–200 mcg/min Dilates coronary arteries and Used to prevent spasm in arterial /
reduces myocardial oxygen grafts after cardiac surgery as
demand, reduce ventricular well as may be used to reduce
pressures preload and afterload
Nitroprusside 0.3–5 mcg/kg/min (high Cause peripheral vasodilation by Used to decreased blood pressure 0/
doses may result in acting directly on smooth and afterload
thiocyanate toxicity) muscle in the venous and
arterial circulation
Norepinephrine 0.01–0.1 mcg/min Stimulation of - and Used for shock and low systemic
/
-adrenergic receptors vascular resistance after
( effects are predominate) cardiac surgery
Phenylephrine 0.1–0.3 mcg/kg/min Potent -adrenergic stimulator Used to increase systemic vascular 0/
resistance and blood pressure
cardiac output is maintained
but blood pressure is low
Vasopressin 0.01–0.1 units/min Potent vasoconstrictor Used to treat shock and increase
systemic vascular resistance and
blood pressure cardiac output
is maintained but blood
pressure is low
, increase; 0, no change; –, decrease.
and phenylephrine may be used A variety of vasodilating agents patients with perioperative MI, troponin I levels peak in 20 hours
35
such as sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, and angiotensin- and at higher concentrations. A study by Lasocki et al. 36 found
converting enzyme inhibitors may be used to reduce afterload in that elevated troponin I levels more than 13 ng/mL was an inde-
low cardiac output syndrome as well as hypertension. Intra-aortic pendent predictor of in-hospital mortality. The interpretation of
balloon pump therapy is frequently used in patients with severe troponin release is complex due to a variety of potential underly-
37
cardiac dysfunction that is not adequately supported with med- ing reasons. New wall-motion abnormalities noted on echocar-
ications alone. diography are another way to verify perioperative MI. Postopera-
tive pericarditis may mimic myocardial ischemia with chest pain
Perioperative Myocardial Infarction. Despite improved and widespread ST-segment elevation. ECG changes associated
methods of myocardial protection, perioperative MI continues to with pericarditis are J-point changes, concave rather than convex,
be a serious complication. Diagnosis of perioperative MI is made and do not result in pathologic Q waves.
from a variety of diagnostic tests including ECG, echocardiogra-
phy, and cardiac enzymes. MI related to cardiac surgery may be Arrhythmias. Arrhythmias are common after cardiac surgery
secondary to spasm of grafts, emboli of air or debris, or insuffi- and are a prevalent cause of increased length of stay after cardiac
cient myocardial protection. CK is routinely elevated immediately surgery. Bradyarrhythmias are common after CABG and valve
after cardiac surgery and usually drops after 12 to 16 hours. CK surgeries and may require temporary pacing via epicardial pacing
peaks associated with perioperative MI occur 16 to 24 hours after wires placed at the time of surgery. Bradycardia or heart block fol-
surgery. More recently, troponin I has been used for the diagnosis lowing cardiac surgery is often hemodynamically significant may
of perioperative MI. Postoperative troponin I levels in patients require placement of permanent transvenous pacers before dis-
without perioperative MI peak at 8 to 10 hours, whereas in charge. Atrial arrhythmias are the most common after cardiac