Page 946 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 946
LWBK340-c42_p921-932.qxd 29/06/2009 11:13 PM Page 922 Aptara
922 PA R T V / Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
cardiovascular care. Elements important to care delivery are dis- significant variation in the heterogeneous variation of disease
cussed. management programs, the American Heart Association devel-
oped taxonomy for disease management that may serve as a guide
to help individuals involved in developing programs and attempt-
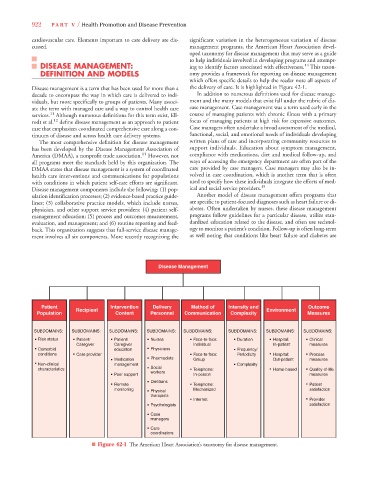
DISEASE MANAGEMENT: ing to identify factors associated with effectiveness. This taxon-
14
DEFINITION AND MODELS omy provides a framework for reporting on disease management
which offers specific details to help the reader note all aspects of
Disease management is a term that has been used for more than a the delivery of care. It is highlighted in Figure 42-1.
decade to encompass the way in which care is delivered to indi- In addition to numerous definitions used for disease manage-
viduals, but more specifically to groups of patients. Many associ- ment and the many models that exist fall under the rubric of dis-
ate the term with managed care and a way to control health care ease management. Case management was a term used early in the
services. 11 Although numerous definitions for this term exist, Ell- course of managing patients with chronic illness with a primary
rodt et al. 12 define disease management as an approach to patient focus of managing patients at high risk for expensive outcomes.
care that emphasizes coordinated comprehensive care along a con- Case managers often undertake a broad assessment of the medical,
tinuum of disease and across health care delivery systems. functional, social, and emotional needs of individuals developing
The most comprehensive definition for disease management written plans of care and incorporating community resources to
has been developed by the Disease Management Association of support individuals. Education about symptom management,
America (DMAA), a nonprofit trade association. 13 However, not compliance with medications, diet and medical follow-up, and
all programs meet the standards held by this organization. The ways of accessing the emergency department are often part of the
DMAA states that disease management is a system of coordinated care provided by case managers. Case managers may also be in-
health care interventions and communications for populations volved in care coordination, which is another term that is often
with conditions in which patient self-care efforts are significant. used to specify how these individuals integrate the efforts of med-
Disease management components include the following: (1) pop- ical and social service providers. 15
ulation identification processes; (2) evidence-based practice guide- Another model of disease management offers programs that
lines; (3) collaborative practice models, which include nurses, are specific to patient-focused diagnoses such as heart failure or di-
physician, and other support service providers; (4) patient self- abetes. Often undertaken by nurses, these disease management
management education; (5) process and outcomes measurement, programs follow guidelines for a particular disease, utilize stan-
evaluation, and management; and (6) routine reporting and feed- dardized education related to the disease, and often use technol-
back. This organization suggests that full-service disease manage- ogy to monitor a patient’s condition. Follow-up is often long-term
ment involves all six components. More recently recognizing the as well noting that conditions like heart failure and diabetes are
Disease Management
Patient Intervention Delivery Method of Intensity and Outcome
Population Recipient Content Personnel Communication Complexity Environment Measures
O
O
S
MAIN
MAIN
S
SUBDOMAINS::SUBDOMAINS:
S
UBD
UBD
SUBDOMAINS::
SUBDOMAINS:
S
MAIN
O
S
SUBDOMAINS:
S
SUBDOMAINS::
MAIN
O
UBD
UBD
SUBDOMAINS:
S
S
O
UBD
SUBDOMAINS:
S SUBDOMAINS:
SUBDOMAINS::
SUBDOMAINS: SUBDOMAINS: SUBDOMAINS:: SUBDOMAINS: SUBDOMAINS: SUBDOMAINS: S SUBDOMAINS: SUBDOMAINS:
MAIN
O
UBD
MAIN
S
SUBDOMAINS::SUBDOMAINS:
S
Risk status Patient/ Patient/ Nurses Face-to-face: Duration Hospital: Clinical
Caregiver Caregiver Individual In-patient measures
Comorbid education Physicians Frequency/
conditions Care provider Face-to-face: Periodicity Hospital: Process
Medication Pharmacists Group Out-patient measures
Non-clinical management Complexity
characteristics Social Telephone: Home-based Quality-of-life
workers
Peer support In-person measures
Dietitians
Remote Telephone: Patient
monitoring Mechanized satisfaction
Physical
therapists
Internet Provider
Psychologists satisfaction
Case
managers
Care
coordinators
■ Figure 42-1 The American Heart Association’s taxonomy for disease management.