Page 125 - untitled
P. 125
AAAC55 21/5/05 10:57 AM Page 124
55 The skull II
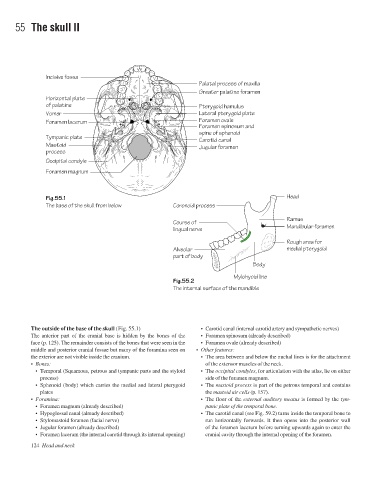
Incisive fossa
Palatal process of maxilla
Greater palatine foramen
Horizontal plate
of palatine Pterygoid hamulus
Vomer Lateral pterygoid plate
Foramen lacerum Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum and
spine of sphenoid
Tympanic plate
Carotid canal
Mastoid Jugular foramen
process
Occipital condyle
Foramen magnum
Fig.55.1 Head
The base of the skull from below Coronoid process
Ramus
Course of
lingual nerve Mandibular foramen
Rough area for
Alveolar medial pterygoid
part of body
Body
Mylohyoid line
Fig.55.2
The internal surface of the mandible
The outside of the base of the skull (Fig. 55.1) • Carotid canal (internal carotid artery and sympathetic nerves)
The anterior part of the cranial base is hidden by the bones of the • Foramen spinosum (already described)
face (p. 125). The remainder consists of the bones that were seen in the • Foramen ovale (already described)
middle and posterior cranial fossae but many of the foramina seen on • Other features:
the exterior are not visible inside the cranium. • The area between and below the nuchal lines is for the attachment
• Bones: of the extensor muscles of the neck.
• Temporal (Squamous, petrous and tympanic parts and the styloid • The occipital condyles, for articulation with the atlas, lie on either
process) side of the foramen magnum.
• Sphenoid (body) which carries the medial and lateral pterygoid • The mastoid process is part of the petrous temporal and contains
plates the mastoid air cells (p. 157).
• Foramina: • The floor of the external auditory meatus is formed by the tym-
• Foramen magnum (already described) panic plate of the temporal bone.
• Hypoglossal canal (already described) • The carotid canal (see Fig. 59.2) turns inside the temporal bone to
• Stylomastoid foramen (facial nerve) run horizontally forwards. It then opens into the posterior wall
• Jugular foramen (already described) of the foramen lacerum before turning upwards again to enter the
• Foramen lacerum (the internal carotid through its internal opening) cranial cavity through the internal opening of the foramen.
124 Head and neck