Page 124 - untitled
P. 124
AAAC54 21/5/05 10:57 AM Page 123
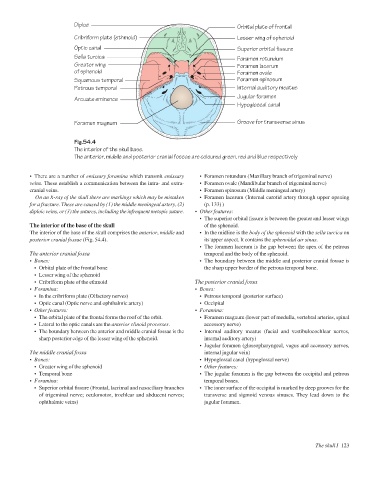
Diploë
Cribriform plate (ethmoid)
Lesser wing of sphenoid
Optic canal Orbital plate of frontal
Superior orbital fissure
Sella turcica Foramen rotundum
Greater wing Foramen lacerum
of sphenoid Foramen ovale
Squamous temporal Foramen spinosum
Petrous temporal Internal auditory meatus
Jugular foramen
Arcuate eminence
Hypoglossal canal
Foramen magnum Groove for transverse sinus
Fig.54.4
The interior of the skull base.
The anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae are coloured green, red and blue respectively
• There are a number of emissary foramina which transmit emissary • Foramen rotundum (Maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve)
veins. These establish a communication between the intra- and extra- • Foramen ovale (Mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve)
cranial veins. • Foramen spinosum (Middle meningeal artery)
On an X-ray of the skull there are markings which may be mistaken • Foramen lacerum (Internal carotid artery through upper opening
for a fracture. These are caused by (1) the middle meningeal artery, (2) (p. 133) )
diploic veins, or (3) the sutures, including the infrequent metopic suture. • Other features:
• The superior orbital fissure is between the greater and lesser wings
The interior of the base of the skull of the sphenoid.
The interior of the base of the skull comprises the anterior, middle and • In the midline is the body of the sphenoid with the sella turcica on
posterior cranial fossae (Fig. 54.4). its upper aspect. It contains the sphenoidal air sinus.
• The foramen lacerum is the gap between the apex of the petrous
The anterior cranial fossa temporal and the body of the sphenoid.
• Bones: • The boundary between the middle and posterior cranial fossae is
• Orbital plate of the frontal bone the sharp upper border of the petrous temporal bone.
• Lesser wing of the sphenoid
• Cribriform plate of the ethmoid The posterior cranial fossa
• Foramina: • Bones:
• In the cribriform plate (Olfactory nerves) • Petrous temporal (posterior surface)
• Optic canal (Optic nerve and ophthalmic artery) • Occipital
• Other features: • Foramina:
• The orbital plate of the frontal forms the roof of the orbit. • Foramen magnum (lower part of medulla, vertebral arteries, spinal
• Lateral to the optic canals are the anterior clinoid processes. accessory nerve)
• The boundary between the anterior and middle cranial fossae is the • Internal auditory meatus (facial and vestibulocochlear nerves,
sharp posterior edge of the lesser wing of the sphenoid. internal auditory artery)
• Jugular foramen (glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves,
The middle cranial fossa internal jugular vein)
• Bones: • Hypoglossal canal (hypoglossal nerve)
• Greater wing of the sphenoid • Other features:
• Temporal bone • The jugular foramen is the gap between the occipital and petrous
• Foramina: temporal bones.
• Superior orbital fissure (Frontal, lacrimal and nasociliary branches • The inner surface of the occipital is marked by deep grooves for the
of trigeminal nerve; oculomotor, trochlear and abducent nerves; transverse and sigmoid venous sinuses. They lead down to the
ophthalmic veins) jugular foramen.
The skull I 123