Page 149 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 149
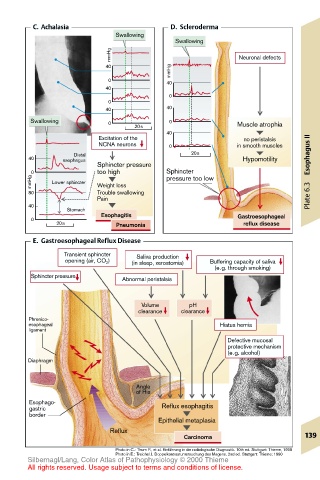
C. Achalasia D. Scleroderma
Swallowing
Swallowing
mmHg Neuronal defects
40
mmHg
0
40
40
0
0
40 40
Swallowing 0 0
20s Muscle atrophia
40
Excitation of the no peristalsis
NCNA neurons 0 in smooth muscles
Distal 20s Esophagus II
40 esophagus Hypomotility
Sphincter pressure
0 too high Sphincter
mmHg Lower sphincter Weight loss pressure too low
80 Trouble swallowing
Pain Plate 6.3
40
Stomach
Esophagitis Gastroesophageal
0
20s Pneumonia reflux disease
E. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Transient sphincter Saliva production
opening (air, CO 2 ) (in sleep, xerostomia) Buffering capacity of saliva
(e.g. through smoking)
Sphincter pressure Abnormal peristalsis
Volume pH
clearance clearance
Phrenico-
esophageal Hiatus hernia
ligament
Defective mucosal
protective mechanism
(e.g. alcohol)
Diaphragm
Angle
of His
Esophago-
gastric Reflux esophagitis
border
Epithelial metaplasia
Reflux
Carcinoma 139
Photo in C.: Thurn P., et al. Einführung in die radiologische Diagnostik. 10th ed. Stuttgart: Thieme, 1998
Photo in E.: Treichel J. Doppelkontrastuntersuchung des Magens. 2nd ed. Stuttgart: Thieme; 1990
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.