Page 151 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 151
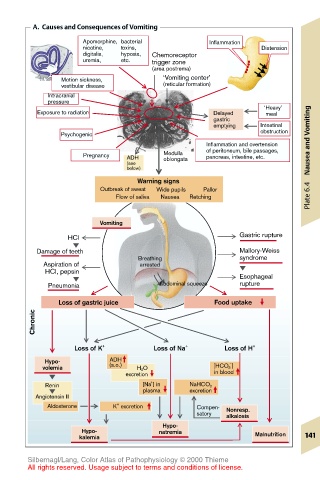
A. Causes and Consequences of Vomiting
Apomorphine, bacterial Inflammation
nicotine, toxins, Distension
digitalis, hypoxia, Chemoreceptor
uremia, etc. trigger zone
(area postrema)
Motion sickness, ‘Vomiting center’
vestibular disease (reticular formation)
Intracranial
pressure
‘Heavy’
Exposure to radiation Delayed meal
gastric
emptying Intestinal
Psychogenic obstruction
Inflammation and overtension Nausea and Vomiting
Pregnancy ADH Medulla of peritoneum, bile passages,
pancreas, intestine, etc.
(see oblongata
below)
Warning signs
Outbreak of sweat Wide pupils Pallor
Flow of saliva Nausea Retching Plate 6.4
Vomiting
HCl Gastric rupture
Damage of teeth Mallory-Weiss
Breathing syndrome
Aspiration of arrested
HCl, pepsin
Esophageal
Pneumonia Abdominal squeeze rupture
Loss of gastric juice Food uptake
Chronic
Loss of K + Loss of Na + Loss of H +
Hypo- ADH –
volemia (s.o.) H 2 O [HCO 3 ]
excretion in blood
+
Renin [Na ] in NaHCO 3
plasma excretion
Angiotensin II
+
Aldosterone K excretion Compen- Nonresp.
satory alkalosis
Hypo-
Hypo- natremia
kalemia Malnutrition 141
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.