Page 229 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 229
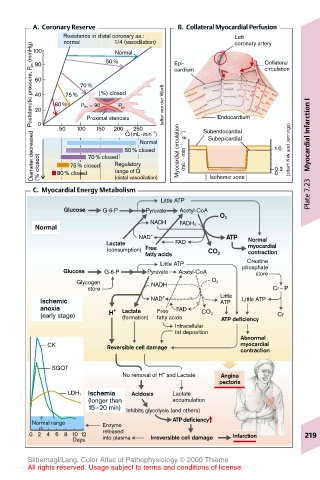
A. Coronary Reserve B. Collateral Myocardial Perfusion
Resistance in distal coronary aa.: Left
normal 50% Epi- coronary artery
1/4 (vasodilation)
Poststenotic pressure, P ps (mmHg) 80 80% 75% 70% (%) closed (after van der Werf) cardium Endocardium circulation
100
Normal
Collateral
60
40
P Ao = 90
P ps
20
Proximal stenosis
100
250
200 .
150
50
–1
Q (mL · min )
Diameter decreased 0 (% closed) 80% closed 70% closed Regulatory Normal Myocardial circulation (mL · min –1 · g –1 ) Subendocardial 1.0 (afterh Kirk and Jennings) Myocardial Infarction I
Subepicardial
50% closed
75% closed
.
0.2
range of Q
0
(distal vasodilation)
C. Myocardial Energy Metabolism Ischemic zone Plate 7.23
Little ATP
Glucose G-6-P Pyruvate Acetyl-CoA
O 2
NADH
Normal FADH 2
NAD + ATP Normal
Lactate FAD myocardial
(consumption) Free
fatty acids CO 2 contraction
Creatine
Little ATP phosphate
Glucose G-6-P Pyruvate Acetyl-CoA store
Glycogen NADH O 2
store Cr∼ P
Ischemic NAD + Little Little ATP
ATP
anoxia + Lactate Free FAD
(early stage) H (formation) fatty acids CO 2 ATP deficiency Cr
Intracellular
fat deposition
Abnormal
CK Reversible cell damage myocardial
contraction
SGOT
+
No removal of H and Lactate Angina
pectoris
Ischemia Acidosis Lactate
LDH 1
(longer than accumulation
15–20 min) Inhibits glycolysis (and others)
ATP deficiency
Normal range Enzyme
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 released Irreversible cell damage Infarction 219
into plasma
Days
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.