Page 225 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 225
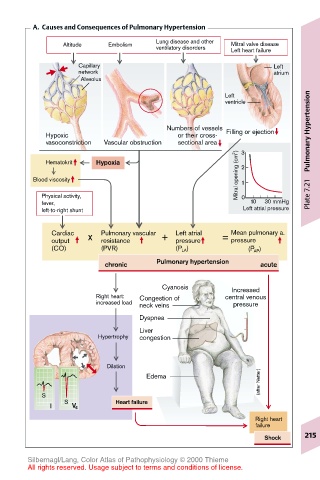
A. Causes and Consequences of Pulmonary Hypertension
Altitude Embolism Lung disease and other Mitral valve disease
ventilatory disorders Left heart failure
Capillary Left
network atrium
Alveolus
Left
ventricle Hypertension
Numbers of vessels
Hypoxic or their cross- Filling or ejection
vasoconstriction Vascular obstruction sectional area 3
Mitral opening (cm 2 )
Hematokrit Hypoxia 2 Pulmonary
Blood viscosity 1
Physical activity, 0 Plate 7.21
fever, 10 30 mmHg
left-to-right shunt Left atrial pressure
Cardiac x Pulmonary vascular + Left atrial = Mean pulmonary a.
output resistance pressure pressure
_
(CO) (PVR) (P LA ) (P AP )
chronic Pulmonary hypertension acute
Cyanosis Increased
Right heart: Congestion of central venous
increased load neck veins pressure
Dyspnea
Liver
Hypertrophy congestion
Dilation
(after Netter)
Edema
S
S Heart failure
I V 6
Right heart
failure
Shock 215
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.