Page 251 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 251
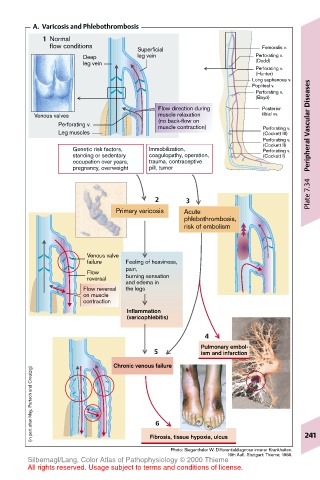
A. Varicosis and Phlebothrombosis
1 Normal
flow conditions Femoralis v.
Superficial
Deep leg vein Perforating v.
leg vein (Dodd)
Perforating v.
(Hunter)
Long saphenous v.
Popliteal v.
Perforating v.
(Boyd)
Flow direction during Posterior
Venous valves muscle relaxation tibial vv.
Perforating v. (no back-flow on Perforating v. Peripheral Vascular Diseases
muscle contraction)
Leg muscles (Cockett III)
Perforating v.
(Cockett II)
Genetic risk factors, Immobilization, Perforating v.
standing or sedentary coagulopathy, operation, (Cockett I)
occupation over years, trauma, contraceptive
pregnancy, overweight pill, tumor
Plate 7.34
2 3
Primary varicosis Acute
phlebothrombosis,
risk of embolism
Venous valve
failure Feeling of heaviness,
pain,
Flow
reversal burning sensation
and edema in
Flow reversal the legs
on muscle
contraction
Inflammation
(varicophlebitis)
4
Pulmonary embol-
5 ism and infarction
Chronic venous failure
(in part after May, Partsch and Creutzig) 6
Fibrosis, tissue hypoxia, ulcus
Photo: Siegenthaler W. Differentialdiagnose innerer Krankheiten. 241
16th Aufl. Stuttgart: Thieme; 1988.
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.