Page 261 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 261
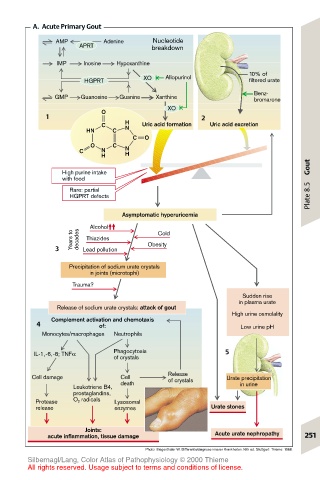
A. Acute Primary Gout
AMP Adenine Nucleotide
APRT breakdown
IMP Inosine Hypoxanthine
10% of
HGPRT XO Allopurinol filtered urate
Benz-
GMP Guanosine Guanine Xanthine bromarone
XO
O
1 2
C H Uric acid formation Uric acid excretion
HN C N
C O
O C
C N N
H H
Gout
High purine intake
with food
Plate 8.5
Rare: partial
HGPRT defects
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Alcohol Cold
Years to decades Thiazides Obesity
3 Lead pollution
Precipitation of sodium urate crystals
in joints (microtophi)
Trauma?
Sudden rise
in plasma urate
Release of sodium urate crystals: attack of gout
High urine osmolality
Complement activation and chemotaxis
4 of: Low urine pH
Monocytes/macrophages Neutrophils
IL-1,-6,-8; TNFα Phagocytosis 5
of crystals
Cell damage Cell Release Urate precipitation
of crystals
Leukotriene B4, death in urine
prostaglandins,
Protease O 2 radicals Lysosomal
release enzymes Urate stones
Joints:
acute inflammation, tissue damage Acute urate nephropathy 251
Photo: Siegenthaler W. Differentialdiagnose innerer Krankheiten.16th ed. Stuttgart: Thieme: 1988.
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.