Page 283 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 283
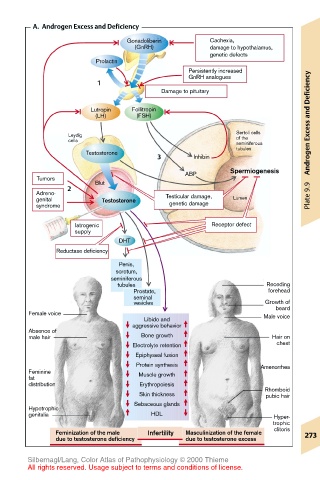
A. Androgen Excess and Deficiency
Gonadoliberin Cachexia,
(GnRH) damage to hypothalamus,
genetic defects
Prolactin
Persistently increased
GnRH analogues
1
Damage to pituitary Deficiency
Lutropin Follitropin
(LH) (FSH) and
Leydig Sertoli cells
of the
cells seminiferous
tubules Androgen Excess
Testosterone
3 Inhibin
Spermiogenesis
ABP
Tumors Blut
2
Adreno-
genital Testosterone Testicular damage, Lumen Plate 9.9
syndrome genetic damage
Iatrogenic Receptor defect
supply
DHT
Reductase deficiency
Penis,
scrotum,
seminiferous
tubules Receding
Prostate, forehead
seminal
vesicles Growth of
beard
Female voice Male voice
Libido and
aggressive behavior
Absence of
male hair Bone growth Hair on
Electrolyte retention chest
Epiphyseal fusion
Protein synthesis Amenorrhea
Feminine
fat Muscle growth
distribution Erythropoiesis
Rhomboid
Skin thickness pubic hair
Sebaceous glands
Hypotrophic
genitalia HDL Hyper-
trophic
Feminization of the male Infertility Masculinization of the female clitoris 273
due to testosterone deficiency due to testosterone excess
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.