Page 106 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 106
Chapter 7 Signaling Transduction and Metabolomics 77
Glutamine Glucose synthesis is necessary for differentiation of T helper 17. Bioactive
lipids have also been profiled in different types of blood cells. For
example, sphingosine-1-phosphate is stored in erythrocytes, and is
Plasma membrane found highly elevated in the blood of sickle cell disease patients owing
to increased erythrocyte sphingosine kinase 1.
Glucose
Glutamine Metabolomics of Nucleotide Metabolism
Polyamines Pentose
Phosphate Measurements of the different polar metabolites in nucleotide
Pathway
metabolism are linked to particular stages of cell growth. For example,
unbiased metabolomics has identified that pyrimidine starvation is a
mechanism for specific types of cell death in multiple myeloma cells.
Amino Acids
Nucleotides
Glutamate Lipids
Metabolomics of Amino Acid Metabolism
Metabolomic studies have revealed that activated T cells reprogram
their metabolism from fatty acid and pyruvate oxidation, and the
TCA cycle, to aerobic glycolysis, the PPP, and glutaminolysis, and
Citrate Pyruvate Lactate metabolic fingerprint similar to tumor cells. In particular, glutamine
is used to increase polyamine biosynthesis, which is essential for T-cell
α-ketoglutarate proliferation, a process controlled by the transcription factor Myc.
TCA SUMMARY AND PERSPECTIVES
Cycle
This short review summarizes the central signaling and metabolic
pathways that play a pivotal role in all the processes executed by
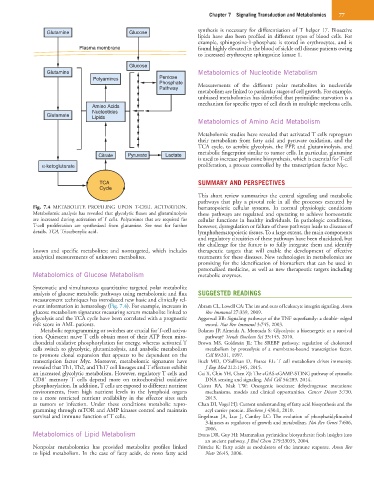
Fig. 7.4 METABOLITE PROFILING UPON T-CELL ACTIVATION. hematopoietic cellular systems. In normal physiologic conditions
Metabolomic analysis has revealed that glycolytic fluxes and glutaminolysis these pathways are regulated and operating to achieve homeostatic
are increased during activation of T cells. Polyamines that are required for cellular functions in healthy individuals. In pathologic conditions,
T-cell proliferation are synthesized from glutamine. See text for further however, dysregulation or failure of these pathways leads to diseases of
details. TCA, Tricarboxylic acid. lymphohematopoietic tissues. To a large extent, the main components
and regulatory circuitries of these pathways have been elucidated, but
the challenge for the future is to fully integrate them and identify
known and specific metabolites; and nontargeted, which includes therapeutic targets that will enable the development of effective
analytical measurements of unknown metabolites. treatments for these diseases. New technologies in metabolomics are
promising for the identification of biomarkers that can be used in
personalized medicine, as well as new therapeutic targets including
Metabolomics of Glucose Metabolism metabolic enzymes.
Systematic and simultaneous quantitative targeted polar metabolite
analysis of glucose metabolic pathways using metabolomic and flux SUGGESTED READINGS
measurement techniques has introduced new basic and clinically rel-
evant information in hematology (Fig. 7.4). For example, increases in Abram CL, Lowell CA: The ins and outs of leukocyte integrin signaling. Annu
glucose metabolism signatures measuring serum metabolite linked to Rev Immunol 27:339, 2009.
glycolysis and the TCA cycle have been correlated with a prognostic Aggarwal BB: Signaling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double- edged
risk score in AML patients. sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745, 2003.
Metabolic reprogramming or switches are crucial for T-cell activa- Bolanos JP, Almeida A, Moncada S: Glycolysis: a bioenergetic or a survival
tion. Quiescent naive T cells obtain most of their ATP from mito- pathway? Trends Biochem Sci 35:145, 2010.
chondrial oxidative phosphorylation for energy, whereas activated T Brown MS, Goldstein JL: The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol
cells switch to glycolytic, glutaminolysis, and anabolic metabolism metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor.
to promote clonal expansion that appears to be dependent on the Cell 89:331, 1997.
transcription factor Myc. Moreover, metabolomic signatures have Buck MD, O’Sullivan D, Pearce EL: T cell metabolism drives immunity.
revealed that Th1, Th2, and Th17 cell lineages and T effectors exhibit J Exp Med 212:1345, 2015.
an increased glycolytic metabolism. However, regulatory T cells and Cai X, Chiu YH, Chen ZJ: The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway of cytosolic
+
CD8 memory T cells depend more on mitochondrial oxidative DNA sensing and signaling. Mol Cell 54:289, 2014.
phosphorylation. In addition, T cells are exposed to different nutrient Cairns RA, Mak TW: Oncogenic isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations:
environments, from high nutrient levels in the lymphoid organs mechanisms, models and clinical opportunities. Cancer Discov 3:730,
to a more restricted nutrient availability in the effector sites such 2013.
as tumors or infection. Under these conditions metabolic repro- Chan DI, Vogel HJ: Current understanding of fatty acid biosynthesis and the
gramming through mTOR and AMP kinases control and maintain acyl carrier protein. Biochem J 430:1, 2010.
survival and immune function of T cells. Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC: The evolution of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 7:606,
2006.
Metabolomics of Lipid Metabolism Evans DR, Guy HI: Mammalian pyrimidine biosynthesis: fresh insights into
an ancient pathway. J Biol Chem 279:33035, 2004.
Nonpolar metabolomics has provided metabolite profiles linked Fritsche K: Fatty acids as modulators of the immune response. Annu Rev
to lipid metabolism. In the case of fatty acids, de novo fatty acid Nutr 26:45, 2006.