Page 1204 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1204
1052 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
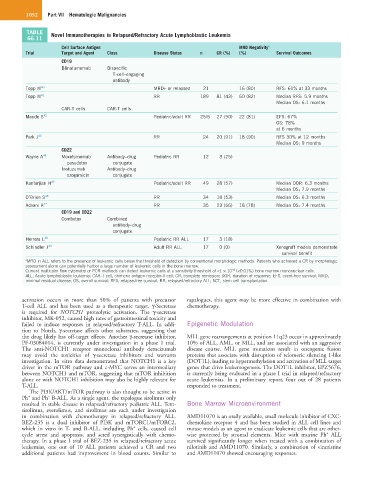
TABLE Novel Immunotherapies in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
66.11
Cell Surface Antigen MRD Negativity a
Trial Target and Agent Class Disease Status n CR (%) (%) Survival Outcomes
CD19
Blinatumomab Bispecific
T-cell–engaging
antibody
Topp M 40 MRD+ or relapsed 21 16 (80) RFS: 61% at 33 months
Topp M 41 RR 189 81 (43) 60 (82) Median RFS: 5.9 months
Median OS: 6.1 months
CAR-T cells CAR-T cells
Maude S 42 Pediatric/adult RR 25/5 27 (90) 22 (81) EFS: 67%
OS: 78%
at 6 months
Park J 43 RR 24 20 (91) 18 (90) RFS 30% at 12 months
Median OS: 9 months
CD22
Wayne A 44 Moxetumomab Antibody–drug Pediatric RR 12 3 (25)
pasudotox conjugate
Inotuzumab Antibody–drug
ozogamicin conjugate
Kantarjian H 45 Pediatric/adult RR 49 28 (57) Median DOR: 6.3 months
Median OS; 7.9 months
O’Brien S 46 RR 34 18 (53) Median OS: 6.3 months
Advani A 47 RR 35 23 (66) 18 (78) Median OS: 7.4 months
CD19 and CD22
Combotox Combined
antibody–drug
conjugate
Herrera L 48 Pediatric RR ALL 17 3 (18)
Schindler J 49 Adult RR ALL 17 0 (0) Xenograft models demonstrate
survival benefit
a MRD in ALL refers to the presence of leukemic cells below the threshold of detection by conventional morphologic methods. Patients who achieved a CR by morphologic
assessment alone can potentially harbor a large number of leukemic cells in the bone marrow.
−4
Current multicolor flow cytometry or PCR methods can detect leukemic cells at a sensitivity threshold of <1 × 10 (<0.01%) bone marrow mononuclear cells.
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CAR-T cell, chimeric antigen receptor-T cell; CR, complete remission; DOR, duration of response; EFS, event-free survival; MRD,
minimal residual disease; OS, overall survival; RFS, relapse-free survival; RR, relapsed/refractory ALL; SCT, stem cell transplantation.
activation occurs in more than 50% of patients with precursor rapalogues, this agent may be more effective in combination with
T-cell ALL and has been used as a therapeutic target. γ-Secretase chemotherapy.
is required for NOTCH1 proteolytic activation. The γ-secretase
inhibitor, MK-052, caused high rates of gastrointestinal toxicity and
failed to induce responses in relapsed/refractory T-ALL. In addi- Epigenetic Modulation
tion to Notch, γ-secretase affects other substrates, suggesting that
the drug likely has off-target effects. Another γ-secretase inhibitor, MLL gene rearrangements at position 11q23 occur in approximately
PF-03084014, is currently under investigation in a phase I trial. 10% of ALL, AML, or MLL, and are associated with an aggressive
The anti-NOTCH1 receptor monoclonal antibody demcizumab disease course. MLL gene mutations result in oncogenic fusion
may avoid the toxicities of γ-secretase inhibitors and warrants proteins that associate with disruption of telomeric silencing 1-like
investigation. In vitro data demonstrated that NOTCH1 is a key (DOT1L), leading to hypermethylation and activation of MLL target
driver in the mTOR pathway and c-MYC serves an intermediary genes that drive leukemogenesis. The DOT1L inhibitor, EPZ5676,
between NOTCH1 and mTOR, suggesting that mTOR inhibition is currently being evaluated in a phase I trial in relapsed/refractory
alone or with NOTCH1 inhibition may also be highly relevant for acute leukemias. In a preliminary report, four out of 28 patients
T-ALL. responded to treatment.
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is also thought to be active in
+
–
Ph and Ph B-ALL. As a single agent, the rapalogue sirolimus only
resulted in stable disease in relapsed/refractory pediatric ALL. Tem- Bone Marrow Microenvironment
sirolimus, everolimus, and sirolimus are each under investigation
in combination with chemotherapy in relapsed/refractory ALL. AMD11070 is an orally available, small molecule inhibitor of CXC-
BEZ-235 is a dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTORC1/mTORC2, chemokine receptor 4 and has been studied in ALL cell lines and
+
which in vitro in T- and B-ALL, including Ph cells, caused cell mouse models as an agent to eradicate leukemic cells that are other-
+
cycle arrest and apoptosis, and acted synergistically with chemo- wise protected by stromal elements. Mice with murine Ph ALL
therapy. In a phase I trial of BEZ-235 in relapsed/refractory acute survived significantly longer when treated with a combination of
leukemias, one out of 10 ALL patients achieved a CR and two nilotinib and AMD11070. Similarly, a combination of vincristine
additional patients had improvement in blood counts. Similar to and AMD11070 showed encouraging responses.