Page 1237 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1237
Chapter 68 The Polycythemias 1083
A B
Cytokine
receptor
JAK2 Cell membrane
V617F
SHP2
NH JH2 JH1 COOH P P P
2 SH2 P P
FERM Pseudokinase Kinase JAK2 JAK2 PIP2 PIP3
domain domain domain
P P PI3K
P P
STAT
GRB2 SHC
AKT
RAS
P P
Trafficking of STAT STAT
cytokine receptors MEK1
ERK
Proliferation
Differentiation Cytoplasm
Survival
GATA1
NF-E2 SOCS
BCL-x
Nucleus CyclinD L
Cytokines/receptors
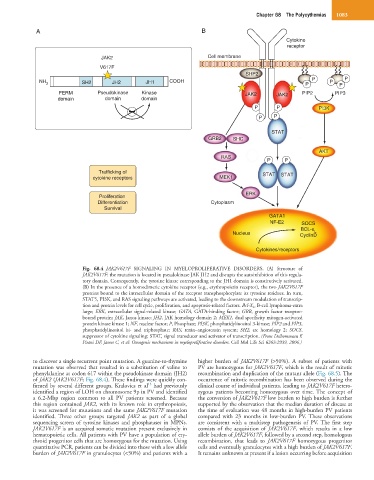
Fig. 68.4 JAK2V617F SIGNALING IN MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS. (A) Structure of
JAK2V617F: the mutation is located in pseudokinase JAK JH2 and disrupts the autoinhibition of this regula-
tory domain. Consequently, the tyrosine kinase corresponding to the JH1 domain is constitutively activated.
(B) In the presence of a homodimeric cytokine receptor (e.g., erythropoietin receptor), the two JAK2V617F
proteins bound to the intracellular domain of the receptor transphosphorylate its tyrosine residues. In turn,
STAT5, PI3K, and RAS signaling pathways are activated, leading to the downstream modulation of transcrip-
tion and protein levels for cell cycle, proliferation, and apoptosis-related factors. Bcl-X L, B-cell lymphoma-extra
large; ERK, extracellular signal-related kinase; GATA, GATA-binding factor; GRB, growth factor receptor-
bound protein; JAK, Janus kinase; JH2, JAK homology domain 2; MEK1, dual specificity mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase 1; NF, nuclear factor; P, Phosphate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2 and PIP3,
phosphatidylinositol bi- and triphosphate; RAS, renin–angiotensin system; SH2, src homology 2; SOCS,
suppressor of cytokine signaling; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription. (From Delhommeau F,
Pisani DF, James C, et al: Oncogenic mechanisms in myeloproliferative disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci 6363:2939, 2006.)
to discover a single recurrent point mutation. A guanine-to-thymine higher burden of JAK2V617F (>50%). A subset of patients with
mutation was observed that resulted in a substitution of valine to PV are homozygous for JAK2V617F, which is the result of mitotic
phenylalanine at codon 617 within the pseudokinase domain (JH2) recombination and duplication of the mutant allele (Fig. 68.5). The
of JAK2 (JAK2V617F; Fig. 68.4). These findings were quickly con- occurrence of mitotic recombination has been observed during the
13
firmed by several different groups. Kralovics et al had previously clinical course of individual patients, leading to JAK2V617F hetero-
identified a region of LOH on chromosome 9p in PV and identified zygous patients becoming homozygous over time. The concept of
a 6.2-Mbp region common to all PV patients screened. Because the conversion of JAK2V617F low burden to high burden is further
this region contained JAK2, with its known role in erythropoiesis, supported by the observation that the median duration of disease at
it was screened for mutations and the same JAK2V617F mutation the time of evaluation was 48 months in high-burden PV patients
identified. Three other groups targeted JAK2 as part of a global compared with 23 months in low-burden PV. These observations
sequencing screen of tyrosine kinases and phosphatases in MPNs. are consistent with a multistep pathogenesis of PV. The first step
JAK2V617F is an acquired somatic mutation present exclusively in consists of the acquisition of JAK2V617F, which results in a low
hematopoietic cells. All patients with PV have a population of ery- allele burden of JAK2V617F, followed by a second step, homologous
throid progenitor cells that are homozygous for the mutation. Using recombination, that leads to JAK2V617F homozygous progenitor
quantitative PCR, patients can be divided into those with a low allele cells and eventually granulocytes with a high burden of JAK2V617F.
burden of JAK2V617F in granulocytes (<50%) and patients with a It remains unknown at present if a lesion occurring before acquisition