Page 1604 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1604
1430 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
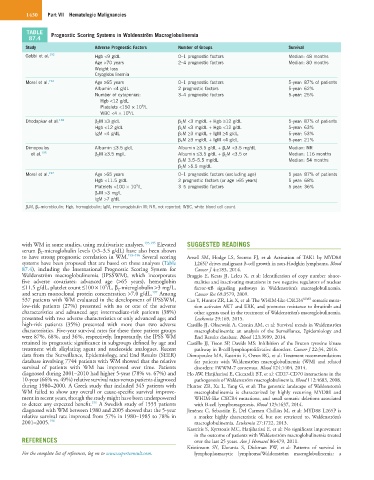
TABLE Prognostic Scoring Systems in Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
87.4
Study Adverse Prognostic Factors Number of Groups Survival
Gobbi et al. 192 Hgb <9 g/dL 0–1 prognostic factors Median: 48 months
Age >70 years 2–4 prognostic factors Median: 80 months
Weight loss
Cryoglobulinemia
Morel et al. 193 Age ≥65 years 0–1 prognostic factors 5-year: 87% of patients
Albumin <4 g/dL 2 prognostic factors 5-year: 62%
Number of cytopenias: 3–4 prognostic factors 5-year: 25%
Hgb <12 g/dL
Platelets <150 × 10 /L
9
WBC <4 × 10 /L
9
Dhodapkar et al. 194 β 2 M ≥3 g/dL β 2 M <3 mg/dL + Hgb ≥12 g/dL 5-year: 87% of patients
Hgb <12 g/dL β 2 M <3 mg/dL + Hgb <12 g/dL 5-year: 63%
IgM <4 g/dL β 2 M ≥3 mg/dL + IgM ≥4 g/dL 5-year: 53%
β 2 M ≥3 mg/dL + IgM <4 g/dL 5-year: 21%
Dimopoulos Albumin ≤3.5 g/dL Albumin ≥3.5 g/dL + β 2 M <3.5 mg/dL Median: NR
et al. 195 β 2 M ≥3.5 mg/L Albumin ≤3.5 g/dL + β 2 M <3.5 or Median: 116 months
β 2 M 3.5–5.5 mg/dL Median: 54 months
β 2 M >5.5 mg/dL
Morel et al. 197 Age >65 years 0–1 prognostic factors (excluding age) 5 year: 87% of patients
Hgb <11.5 g/dL 2 prognostic factors (or age >65 years) 5 year: 68%
Platelets <100 × 10 /L 3–5 prognostic factors 5 year: 36%
9
β 2 M >3 mg/L
IgM >7 g/dL
β 2 M, β 2 -microbloulin; Hgb, hemoglobulin; IgM, immunoglobulin M; NR, not reported; WBC, white blood cell count.
with WM in some studies, using multivariate analyses. 193,195 Elevated SUGGESTED READINGS
serum β 2 -microglobulin levels (>3–3.5 g/dL) have also been shown
to have strong prognostic correlation in WM. 193–196 Several scoring Ansell SM, Hodge LS, Secreto FJ, et al: Activation of TAK1 by MYD88
systems have been proposed that are based on these analyses (Table L265P drives malignant B-cell growth in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood
87.4), including the International Prognostic Scoring System for Cancer J 4:e183, 2014.
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (IPSSWM), which incorporates Braggio E, Keats JJ, Leleu X, et al: Identification of copy number abnor-
five adverse covariates: advanced age (>65 years), hemoglobin malities and inactivating mutations in two negative regulators of nuclear
9
≤11.5 g/dL, platelet count ≤100 × 10 /L, β 2 -microglobulin >3 mg/L, factor-κB signaling pathways in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia.
197
and serum monoclonal protein concentration >7.0 g/dL. Among Cancer Res 69:3579, 2009.
537 patients with WM evaluated in the development of IPSSWM, Cao Y, Hunter ZR, Liu X, et al: The WHIM-like CXCR4 S338X somatic muta-
low-risk patients (27%) presented with no or one of the adverse tion activates AKT and ERK, and promotes resistance to ibrutinib and
characteristics and advanced age; intermediate-risk patients (38%) other agents used in the treatment of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia.
presented with two adverse characteristics or only advanced age; and Leukemia 29:169, 2015.
high-risk patients (35%) presented with more than two adverse Castillo JJ, Olszewski A, Cronin AM, et al: Survival trends in Waldenström
characteristics. Five-year survival rates for these three patient groups macroglobulinemia: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and
were 87%, 68%, and 36%, respectively. Importantly, the IPSS WM End Results database. Blood 123:3999, 2014.
retained its prognostic significance in subgroups defined by age and Castillo JJ, Treon SP, Davids MS: Inhibition of the Bruton tyrosine kinase
treatment with alkylating agent and nucleoside analogues. Recent pathway in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Cancer J 22:34, 2016.
data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis E, Owen RG, et al: Treatment recommendations
database involving 7744 patients with WM showed that the relative for patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) and related
survival of patients with WM has improved over time. Patients disorders: IWWM-7 consensus. Blood 124:1404, 2014.
diagnosed during 2001–2010 had higher 5-year (78% vs. 67%) and Ho AW, Hatjiharissi E, Ciccarelli BT, et al: CD27-CD70 interactions in the
10-year (66% vs. 49%) relative survival rates versus patients diagnosed pathogenesis of Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 112:4683, 2008.
during 1980–2000. A Greek study that included 345 patients with Hunter ZR, Xu L, Yang G, et al: The genomic landscape of Waldenstom’s
WM failed to show any overall or cause-specific survival improve- macroglobulinemia is characterized by highly recurring MYD88 and
ment in recent years, though the study might have been underpowered WHIM-like CXCR4 mutations, and small somatic deletions associated
196
to detect any expected benefit. A Swedish study of 1555 patients with B-cell lymphomagenesis. Blood 123:1637, 2014.
diagnosed with WM between 1980 and 2005 showed that the 5-year Jiménez C, Sebastián E, Del Carmen Chillón M, et al: MYD88 L265P is
relative survival rate improved from 57% in 1980–1985 to 78% in a marker highly characteristic of, but not restricted to, Waldenström’s
2001–2005. 198 macroglobulinemia. Leukemia 27:1722, 2013.
Kastritis S, Kyrtsonis MC, Hatjiharissi E, et al: No significant improvement
in the outcome of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia treated
REFERENCES over the last 25 years. Am J Hematol 86:479, 2011.
Kristinsson SY, Eloranta S, Dickman PW, et al: Patterns of survival in
For the complete list of references, log on to www.expertconsult.com. lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia: a