Page 1717 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1717
Chapter 95 Practical Aspects of Hematologic Stem Cell Harvesting and Mobilization 1527
+
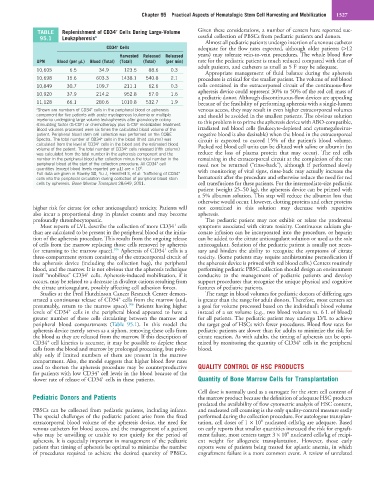
TABLE Replenishment of CD34 Cells During Large-Volume Given these considerations, a number of centers have reported suc-
95.1 Leukapheresis a cessful collection of PBSCs from pediatric patients and donors.
Almost all pediatric patients undergo insertion of a venous catheter
+
CD34 Cells adequate for the flow rates expected, although older patients (>12
Harvested Released Released years) may tolerate vein-to-vein procedures. The whole blood flow
UPN Blood (per µL) Blood (Total) (Total) (Total) (per min) rate for the pediatric patient is much reduced compared with that of
adult patients, and catheters as small as 5 F may be adequate.
10,605 6.5 34.9 123.5 88.6 0.3
Appropriate management of fluid balance during the apheresis
10,698 15.6 603.3 1438.1 540.8 2.1 procedure is critical for the smaller patient. The volume of red blood
10,849 30.7 109.7 211.1 62.6 0.3 cells contained in the extracorporeal circuit of the continuous-flow
apheresis device could represent 30% to 50% of the red cell mass of
10,920 37.9 214.2 952.8 57.0 1.6
a pediatric donor. Although discontinuous-flow devices are appealing
11,128 66.1 280.6 1010.8 532.7 1.9 because of the feasibility of performing apheresis with a single-lumen
a Shown are numbers of CD34 cells in the peripheral blood or apheresis venous access, they may result in even higher extracorporeal volumes
+
component for five patients with acute myelogenous leukemia or multiple and should be avoided in the smallest patients. The obvious solution
myeloma undergoing large-volume leukapheresis after granulocyte colony- to this problem is to prime the apheresis device with ABO-compatible,
stimulating factor (G-CSF) or chemotherapy plus G-CSF mobilization treatment.
Blood volumes processed were six times the calculated blood volume of the irradiated red blood cells (leukocyte-depleted and cytomegalovirus-
patient. Peripheral blood stem cell collection was performed on the COBE negative blood is also desirable) when the blood in the extracorporeal
Spectra. The total number of CD34 cells in the blood (third column) was circuit is expected to exceed 15% of the patient’s blood volume.
+
+
calculated from the level of CD34 cells in the blood and the estimated blood Packed red blood cell units can be diluted with saline or albumin (to
+
volume of the patient. The total number of CD34 cells released (fifth column)
was calculated from the total number in the apheresis component and the reduce the loss of plasma protein that may occur). The red cells
number in the peripheral blood after collection minus the total number in the remaining in the extracorporeal circuit at the completion of the run
+
peripheral blood at the start of the collection procedure. All CD34 cell need not be returned (“rinse-back”), although if performed slowly
quantities (except blood levels reported per µL) are × 10 . 6 with monitoring of vital signs, rinse-back may actually increase the
Full data are given in Rowley SD, Yu J, Heimfeld S, et al: Trafficking of CD34 +
cells into the peripheral circulation during collection of peripheral blood stem hematocrit after the procedure and otherwise reduce the need for red
cells by apheresis. Bone Marrow Transplant 28:649, 2001. cell transfusions for these patients. For the intermediate-size pediatric
patient (weight 25–50 kg), the apheresis device can be primed with
a 5% albumin solution. This step will reduce the albumin loss that
otherwise would occur. However, clotting proteins and other proteins
higher risk for citrate (or other anticoagulant) toxicity. Patients will not contained in this solution may decrease with repetitive
also incur a proportional drop in platelet counts and may become apheresis.
profoundly thrombocytopenic. The pediatric patient may not exhibit or relate the prodromal
+
Most reports of LVL describe the collection of more CD34 cells symptoms associated with citrate toxicity. Continuous calcium glu-
than are calculated to be present in the peripheral blood at the initia- conate infusion can be incorporated into the procedure, or heparin
tion of the apheresis procedure. This results from the ongoing release can be added to the citrate anticoagulant solution or used as the sole
of cells from the marrow replacing those cells removed by apheresis anticoagulant. Sedation of the pediatric patient is usually not neces-
+
106
(or returning to the marrow space). Apheresis of CD34 cells is a sary and hinders the ability to recognize the symptoms of citrate
three-compartment system consisting of the extracorporeal circuit of toxicity. (Some patients may require antihistamine premedication if
the apheresis device (including the collection bag), the peripheral the apheresis device is primed with red blood cells.) Centers routinely
blood, and the marrow. It is not obvious that the apheresis technique performing pediatric PBSC collection should design an environment
+
itself “mobilizes” CD34 cells. Apheresis-induced mobilization, if it conducive to the management of pediatric patients and develop
occurs, may be related to a decrease in divalent cations resulting from support procedures that recognize the unique physical and cognitive
the citrate anticoagulant, possibly affecting cell adhesion forces. features of pediatric patients.
Studies at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center demon- The range in blood volumes for pediatric donors of differing ages
+
strated a continuous release of CD34 cells from the marrow (and, is greater than the range for adult donors. Therefore, most centers set
106
presumably, return to the marrow space). Patients having higher a goal for volume processed based on the individual’s blood volume
+
levels of CD34 cells in the peripheral blood appeared to have a instead of a set volume (e.g., two blood volumes vs. 6 L of blood)
greater number of these cells circulating between the marrow and for all patients. The pediatric patient may undergo LVL to achieve
peripheral blood compartments (Table 95.1). In this model the the target goal of HSCs with fewer procedures. Blood flow rates for
apheresis device merely serves as a siphon, removing these cells from pediatric patients are slower than for adults to minimize the risk for
the blood as they are released from the marrow. If this description of citrate reaction. As with adults, the timing of apheresis can be opti-
+
+
CD34 cell kinetics is accurate, it may be possible to deplete these mized by monitoring the quantity of CD34 cells in the peripheral
cells from the blood and marrow by prolonged processing, but prob- blood.
ably only if limited numbers of them are present in the marrow
compartment. Also, the model suggests that higher blood flow rates
used to shorten the apheresis procedure may be counterproductive QUALITY CONTROL OF HSC PRODUCTS
+
for patients with low CD34 cell levels in the blood because of the
+
slower rate of release of CD34 cells in these patients. Quantity of Bone Marrow Cells for Transplantation
Cell dose is normally used as a surrogate for the stem cell content of
Pediatric Donors and Patients the marrow product because the definition of adequate HSC products
predated the availability of flow cytometric analysis of HSC content,
PBSCs can be collected from pediatric patients, including infants. and nucleated cell counting is the only quality-control measure easily
The special challenges of the pediatric patient arise from the fixed performed during the collection procedure. For autologous transplan-
8
extracorporeal blood volume of the apheresis device, the need for tation, cell doses of 1 × 10 nucleated cells/kg are adequate. Based
venous catheters for blood access, and the management of a patient on early reports that smaller quantities increased the risk for engraft-
8
who may be unwilling or unable to rest quietly for the period of ment failure, most centers target 3 × 10 nucleated cells/kg of recipi-
apheresis. It is especially important in management of the pediatric ent weight for allogeneic transplantation. However, those early
patient that timing of apheresis be optimal to minimize the number reports were of patients being treated for aplastic anemia, in which
of procedures required to achieve the desired quantity of PBSCs. engraftment failure is a more common event. A review of unrelated